Obesity and underweight are associated with an increased risk of death after lung transplantation
- PMID: 19608717
- PMCID: PMC2773915
- DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200903-0425OC
Obesity and underweight are associated with an increased risk of death after lung transplantation
Abstract
Rationale: Obesity is considered a relative contraindication to lung transplantation, based on studies that have not accounted for key confounders. Little is known about the risk of death for underweight candidates after transplantation.
Objectives: To examine the associations of pretransplant obesity and underweight with the risk of death after lung transplantation.
Methods: We examined 5,978 adults with cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and diffuse parenchymal lung disease who underwent lung transplantation in the United States between 1995 and 2003. We used Cox models and generalized additive models to examine the association between pretransplant body mass index and the risk of death after lung transplantation with adjustment for donor and recipient factors.
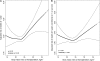
Measurements and main results: The median follow-up time was 4.2 years. Compared with normal weight recipients, the multivariable-adjusted rates of death were 15% higher for underweight recipients (95% confidence interval, 3 to 28%), 15% higher for overweight recipients (95% confidence interval, 6 to 26%), and 22% higher for obese recipients (95% confidence interval, 8 to 39%). These relationships persisted when stratified by diagnosis. The multivariable-adjusted population attributable fraction was 12% at 1 year and 8% at 5 years.
Conclusions: Both obesity and underweight are independent risk factors for death after lung transplantation, contributing to up to 12% of deaths in the first year after transplantation. Primary care providers and pulmonologists should promote a healthy weight for patients with lung disease long before transplantation is considered.
Figures


References
-
- Orens JB, Estenne M, Arcasoy S, Conte JV, Corris P, Egan JJ, Egan T, Keshavjee S, Knoop C, Kotloff R, et al. International guidelines for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2006 update–a consensus report from the Pulmonary Scientific Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:745–755. - PubMed
-
- Hertz MI, Taylor DO, Trulock EP, Boucek MM, Mohacsi PJ, Edwards LB, Keck BM. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: nineteenth official report—2002. J Heart Lung Transplant 2002;21:950–970. - PubMed
-
- Trulock EP, Edwards LB, Taylor DO, Boucek MM, Keck BM, Hertz MI. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-second official adult lung and heart–lung transplant report−2005. J Heart Lung Transplant 2005;24:956–967. - PubMed
-
- Trulock EP, Edwards LB, Taylor DO, Boucek MM, Keck BM, Hertz MI. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-third official adult lung and heart–lung transplantation report−2006. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25:880–892. - PubMed
-
- Trulock EP, Christie JD, Edwards LB, Boucek MM, Aurora P, Taylor DO, Dobbels F, Rahmel AO, Keck BM, Hertz MI. Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: twenty-fourth official adult lung and heart–lung transplantation report—2007. J Heart Lung Transplant 2007;26:782–795. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

