Stabilizing immature breathing patterns of preterm infants using stochastic mechanosensory stimulation
- PMID: 19608934
- PMCID: PMC2763836
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00058.2009
Stabilizing immature breathing patterns of preterm infants using stochastic mechanosensory stimulation
Abstract
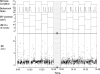
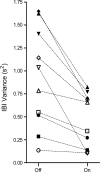
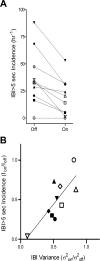
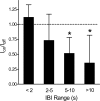
Breathing patterns in preterm infants consist of highly variable interbreath intervals (IBIs) that might originate from nonlinear properties of the respiratory oscillator and its input-output responses to peripheral and central signals. Here, we explore a property of nonlinear control, the potential for large improvement in the stability of breathing using low-level exogenous stochastic stimulation. Stimulation was administered to 10 preterm infants (postconceptional age: mean 33.3 wk, SD 1.7) using a mattress with embedded actuators that delivered small stochastic displacements (0.021 mm root mean square, 0.090 mm maximum, 30-60 Hz); this stimulus was subthreshold for causing arousal from sleep to wakefulness or other detectable changes in the behavioral state evaluated with polysomnography. We used a test-retest protocol with multiple 10-min intervals of stimulation, each paired with 10-min intervals of no stimulation. Stimulation induced an approximately 50% reduction (P = 0.003) in the variance of IBIs and an approximately 50% reduction (P = 0.002) in the incidence of IBIs > 5 s. The improved stability of eupneic breathing was associated with an approximately 65% reduction (P = 0.04) in the duration of O(2) desaturation. Our findings suggest that nonlinear properties of the immature respiratory control system can be harnessed using afferent stimuli to stabilize eupneic breathing, thereby potentially reducing the incidence of apnea and hypoxia.
Figures
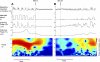
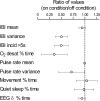
Comment in
-
What to do about apnea of prematurity?J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009 Oct;107(4):1015-6. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00940.2009. Epub 2009 Aug 20. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2009. PMID: 19696360 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abu-Osba YK, Brouillette RT, Wilson SL, Thach BT. Breathing pattern and transcutaneous oxygen tension during motor activity in preterm infants. Am Rev Respir Dis 125: 382–387, 1982 - PubMed
-
- Abu-Shaweesh JM, Martin RJ. Neonatal apnea: what's new? Pediatr Pulmonol 43: 937–944, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Al-Saif S, Alvaro R, Manfreda J, Kwiatkowski K, Cates D, Qurashi M, Rigatto H. A randomized controlled trial of theophylline versus CO2 inhalation for treating apnea of prematurity. J Pediatr 153: 513–518, 2008 - PubMed
-
- Bennett MJ, Lawrence RJ. Trials with the auditory response cradle. II. The neonatal respiratory response to an auditory stimulus. Br J Audiol 14: 1–6, 1980 - PubMed
-
- Bruce EN. Temporal variations in the pattern of breathing. J Appl Physiol 80: 1079–1087, 1996 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

