Structure and function of HDL mimetics
- PMID: 19608977
- PMCID: PMC2860541
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.187518
Structure and function of HDL mimetics
Abstract
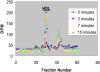
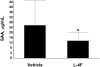
HDL mimetics have been constructed from a number of peptides and proteins with varying structures, all of which bind lipids found in HDL. HDL mimetics containing a peptide or protein have been constructed with as few as 4 and as many as 243 amino acid residues. Some HDL mimetics have been constructed with lipid but without a peptide or protein component. Some HDL mimetics promote cholesterol efflux, some have been shown to have a remarkable ability to bind oxidized lipids compared to human apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I). Many of these peptides have been shown to have antiinflammatory properties. Based on studies in a number of animal models and in early human clinical trials, HDL mimetics appear to have promise as diagnostic and therapeutic agents.
Figures
References
-
- Briel M, Ferreira-Gonzalez I, You JJ, Karanicolas PJ, Akl EA, Wu P, Belchacz B, Bassler D, Wei X, Sharman A, Whitt I, da Silva SA, Khalid Z, Nordmannn AJ, Zhou Q, Walter SD, Vale N, Bhatnagar N, O’Regan C, Mills EJ, Bucher HC, Montori VM, Guyatt GH. Association between change in high density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. British Medical Journal. 2009;338:b92. [PubMed – in process] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng L, Nukuna B, Brennan M-L, Sun M, Goormastic M, Settle M, Schmitt D, Fu X, Thomson L, Fox PL, Ischiropoulos H, Smith JD, Kinter M, Hazen SL. Apolipoprotein A-I is a selective target for myeloperoxidase –catalyzed oxidation and functional impairment in subjects with cardiovascular disease. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:529–541. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Singh IM, Shishehbor MH, Ansell BJ. High-density lipoprotein as a therapeutic target: a systematic review. JAMA. 2007;298:786–798. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

