Crosstalk of Notch with p53 and p63 in cancer growth control
- PMID: 19609265
- PMCID: PMC6059364
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc2675
Crosstalk of Notch with p53 and p63 in cancer growth control
Abstract
Understanding the complexity of cancer depends on an elucidation of the underlying regulatory networks, at the cellular and intercellular levels and in their temporal dimension. This Opinion article focuses on the multilevel crosstalk between the Notch pathway and the p53 and p63 pathways. These two coordinated signalling modules are at the interface of external damaging signals and control of stem cell potential and differentiation. Positive or negative reciprocal regulation of the two pathways can vary with cell type and cancer stage. Therefore, selective or combined targeting of the two pathways could improve the efficacy and reduce the toxicity of cancer therapies.
Figures
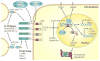


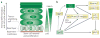
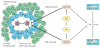
References
-
- Stelling J, Sauer U, Szallasi Z, Doyle FJ, Doyle J. Robustness of cellular functions. Cell. 2004;118:675–685. - PubMed
-
- Alon U. Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nature Rev Genet. 2007;8:450–461. - PubMed
-
- Bray SJ. Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nature Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:678–689. - PubMed
-
- Hurlbut GD, Kankel MW, Lake RJ, Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Crossing paths with Notch in the hyper-network. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2007;19:166–175. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

