An ER-resident membrane protein complex regulates nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit composition at the synapse
- PMID: 19609303
- PMCID: PMC2738700
- DOI: 10.1038/emboj.2009.204
An ER-resident membrane protein complex regulates nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit composition at the synapse
Abstract
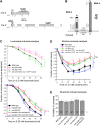
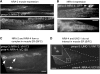
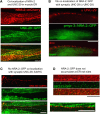
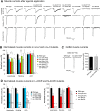
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) are homo- or heteropentameric ligand-gated ion channels mediating excitatory neurotransmission and muscle activation. Regulation of nAChR subunit assembly and transfer of correctly assembled pentamers to the cell surface is only partially understood. Here, we characterize an ER transmembrane (TM) protein complex that influences nAChR cell-surface expression and functional properties in Caenorhabditis elegans muscle. Loss of either type I TM protein, NRA-2 or NRA-4 (nicotinic receptor associated), affects two different types of muscle nAChRs and causes in vivo resistance to cholinergic agonists. Sensitivity to subtype-specific agonists of these nAChRs is altered differently, as demonstrated by whole-cell voltage-clamp of dissected adult muscle, when applying exogenous agonists or after photo-evoked, channelrhodopsin-2 (ChR2) mediated acetylcholine (ACh) release, as well as in single-channel recordings in cultured embryonic muscle. These data suggest that nAChRs desensitize faster in nra-2 mutants. Cell-surface expression of different subunits of the 'levamisole-sensitive' nAChR (L-AChR) is differentially affected in the absence of NRA-2 or NRA-4, suggesting that they control nAChR subunit composition or allow only certain receptor assemblies to leave the ER.
Figures

References
-
- Changeux J, Edelstein S (2005) Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. New York: Odile Jacob Publishing Corporation
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

