Differential use of an in-frame translation initiation codon regulates human mu opioid receptor (OPRM1)
- PMID: 19609488
- PMCID: PMC11115551
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-009-0082-7
Differential use of an in-frame translation initiation codon regulates human mu opioid receptor (OPRM1)
Abstract
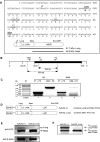
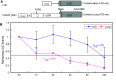
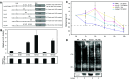
The pharmacological effects of morphine and morphine-like drugs are mediated primarily through the micro opioid receptor. Here we show that differential use of an in-frame translational start codon in the 5'-untranslated region of the OPRM1 generates different translational products in vivo and in vitro. The 5'-end of the OPRM1 gene is necessary for initiating the alternate form and for subsequent degradation of the protein. Initiation of OPRM1 at the upstream site decreases the initiation at the main AUG site. However, alternative initiation of the long form of OPRM1 produces a protein with a short half-life, resulting from degradation mediated by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Reporter and degradation assays showed that mutations of this long form at the second and third lysines reduce ubiquitin-dependent proteasome degradation, stabilizing the protein. The data suggest that MOP expression is controlled in part by initiation of the long form of MOP at the alternate site.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA011190/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA013926/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA070554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA001583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA000564/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA001583/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- DA013926/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA011190/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05-DA070554/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

