Preclinical characterization of Aurora kinase inhibitor R763/AS703569 identified through an image-based phenotypic screen
- PMID: 19609559
- PMCID: PMC11827822
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0641-1
Preclinical characterization of Aurora kinase inhibitor R763/AS703569 identified through an image-based phenotypic screen
Abstract
Purpose: Aurora kinases play a key role in mitotic progression. Over-expression of Aurora kinases is found in several human cancers and correlated with histological malignancy and clinical outcomes. Therefore, Aurora kinase inhibitors should be useful in the treatment of cancers.
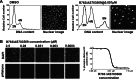
Methods: Cell-based screening methods have an advantage over biochemical approaches because hits can be optimized to inhibit targets in the proper intracellular context. We developed a novel Aurora kinase inhibitor R763/AS703569 using an image-based phenotypic screen. The anti-proliferative effect was examined in a panel of tumor cell lines and primary cells. The efficacy was determined in a broad panel of xenograft models.
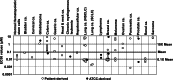
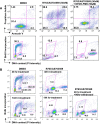
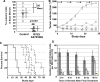
Results: R763/AS703569 inhibits Aurora kinases, along with a limited number of other kinases including FMS-related tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3), and has potent anti-proliferative activity against many cell types accompanying unique phenotypic changes such as enlarged cell size, endoreduplication and apoptosis. The endoreduplication cycle induced by R763/AS703569 was irreversible even after the compound was withdrawn from the culture. Oral administration of R763/AS703569 demonstrated marked inhibition of tumor growth in xenograft models of pancreatic, breast, colon, ovarian, and lung tumors and leukemia. An acute myeloid leukemia cell line MV4-11, which carries a FLT3 internal tandem duplication mutation, is particularly sensitive to R763/AS703569 in vivo.
Conclusions: R763/AS703569 is a potent inhibitor of Aurora kinases and exhibited significant anti-proliferative activity against a wide range of tumor cells both in vitro and in vivo. Inhibition of Aurora kinases has the potential to be a new addition to the treatment of cancers.
Figures

References
-
- Adams RR, Wheatley SP, Gouldsworthy AM, Kandels-Lewis SE, Carmena M, Smythe C et al (2000) INCENP binds the Aurora-related kinase AIRK2 and is required to target it to chromosomes, the central spindle and cleavage furrow. Curr Biol 10(17):1075–1078 - PubMed
-
- Araki K, Nozaki K, Ueba T, Tatsuka M, Hashimoto N (2004) High expression of Aurora-B/Aurora and Ipll-like midbody-associated protein (AIM-1) in astrocytomas. J Neurooncol 67(1–2):53–64 - PubMed
-
- Barabasz A, Foley B, Otto JC, Scott A, Rice J (2006) The use of high-content screening for the discovery and characterization of compounds that modulate mitotic index and cell cycle progression by differing mechanisms of action. Assay Drug Dev Technol 4(2):153–163 - PubMed
-
- Bayliss R, Sardon T, Vernos I, Conti E (2003) Structural basis of Aurora-A activation by TPX2 at the mitotic spindle. Mol Cell 12(4):851–862 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

