Application of 31P NMR spectroscopy and chemical derivatization for metabolite profiling of lipophilic compounds in human serum
- PMID: 19610016
- PMCID: PMC2861047
- DOI: 10.1002/mrc.2480
Application of 31P NMR spectroscopy and chemical derivatization for metabolite profiling of lipophilic compounds in human serum
Abstract
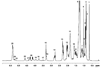
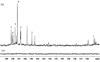
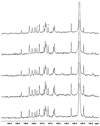
New methods for obtaining metabolic fingerprints of biological samples with improved resolution and sensitivity are highly sought for early disease detection, studies of human health and pathophysiology, and for better understanding systems biology. Considering the complexity of biological samples, interest in biochemical class selection through the use of chemoselective probes for improved resolution and quantitation is increasing. Considering the role of lipids in the pathogenesis of a number of diseases, in this study fingerprinting of lipid metabolites was achieved by (31)P labeling using the derivatizing agent 2-chloro-4,4,5,5-tetramethyldioxaphospholane. Lipids containing hydroxyl, aldehyde and carboxyl groups were selectively tagged with (31)P and then detected with good resolution using (31)P NMR by exploiting the 100% natural abundance and wide chemical shift range of (31)P. After standardizing the reaction conditions using representative compounds, the derivatization approach was used to profile lipids in human serum. The results show that the (31)P derivatization approach is simple, reproducible and highly quantitative, and has the potential to profile a number of important lipids in complex biological samples.
Figures

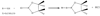
References
-
- Otvos JD, Jeyarajah EJ, Bennett DW. Quantification of Plasma-Lipoproteins by Proton Nuclear-Magnetic-Resonance Spectroscopy. Clinical Chemistry. 1991;37(3):377–386. - PubMed
-
- Shah FD, Shukla SN, Shah PM, Patel HRH, Patel PS. Significance of alterations in plasma lipid profile levels in breast cancer. Integrative Cancer Therapies. 2008;7(1):33–41. - PubMed
-
- Andreotti G, Chen JB, Gao YT, Rashid A, Chang SC, Shen MC, Wang BS, Han TQ, Zhang BH, Danforth KN, Althuis MD, Hsing AW. Serum lipid levels and the risk of biliary tract cancers and biliary stones: A population-based study in China. International Journal of Cancer. 2008;122(10):2322–2329. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tukiainen T, Tynkkynen T, Makinen VP, Jylanki P, Kangas A, Hokkanen J, Vehtari A, Grohn O, Hallikainen M, Soininen H, Kivipelto M, Groop PH, Kaski K, Laatikainen R, Soininen P, Pirttila T, Ala-Korpela M. A multi-metabolite analysis of serum by H-1 NMR spectroscopy: Early systemic signs of Alzheimer's disease. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 2008;375(3):356–361. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

