Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach
- PMID: 19610618
- PMCID: PMC2888655
- DOI: 10.1021/jm9002395
Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF1R) tyrosine kinase as a novel cancer therapy approach
Figures
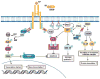
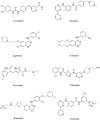
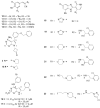
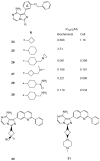
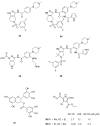
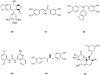
Similar articles
-
The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor pathway.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Oct 15;14(20):6364-70. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-4879. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18927274 Review.
-
Targeting the type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor as anti-cancer treatment.Anticancer Drugs. 2003 Oct;14(9):669-82. doi: 10.1097/00001813-200310000-00001. Anticancer Drugs. 2003. PMID: 14551500 Review.
-
Insulin-like growth factor receptor signaling in tumorigenesis and drug resistance: a challenge for cancer therapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Jun 3;13(1):64. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00904-3. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32493414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IGF1R signalling and its inhibition.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006 Dec;13 Suppl 1:S33-43. doi: 10.1677/erc.1.01280. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2006. PMID: 17259557 Review.
-
Activation of the insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor induces resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor antagonism in head and neck squamous carcinoma cells.Mol Cancer Ther. 2011 Nov;10(11):2124-34. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0294. Epub 2011 Aug 30. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011. PMID: 21878657 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
TGFβ signaling in myeloid cells regulates mammary carcinoma cell invasion through fibroblast interactions.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 28;10(1):e0117908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0117908. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25629162 Free PMC article.
-
Let-7c inhibits migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by targeting IGF1R and HMGA2.Oncotarget. 2018 Jan 2;9(10):8927-8940. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23826. eCollection 2018 Feb 6. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29507664 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on New Functions of Animal and Plant Proteins.Foods. 2024 Apr 17;13(8):1223. doi: 10.3390/foods13081223. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38672894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumor efficacy of the heparan sulfate mimic roneparstat (SST0001) against sarcoma models involves multi-target inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinases.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47848-47863. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10292. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27374103 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual screening of specific insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) inhibitors from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) molecular database.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Dec 14;13(12):17185-209. doi: 10.3390/ijms131217185. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23242155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Salmon WD, Jr, Daughaday WH. A hormonally controlled serum factor which stimulates sulfate incorporation by cartilage in vitro. J Lab Clin Med. 1957;49:825–836. - PubMed
-
- Bell GI, Pictet RL, Rutter WJ, Cordell B, Tischer E, Goodman HM. Sequence of the human insulin gene. Nature. 1980;284:26–32. - PubMed
-
- Dull TJ, Gray A, Hayflick JS, Ullrich A. Insulin-like growth factor II precursor gene organization in relation to insulin gene family. Nature. 1984;310:777–781. - PubMed
-
- Jansen M, van Schaik FM, Ricker AT, Bullock B, Woods DE, Gabbay KH, Nussbaum AL, Sussenbach JS, Van den Brande JL. Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth factor I precursor. Nature. 1983;306:609–611. - PubMed
-
- Ullrich A, Dull TJ, Gray A, Brosius J, Sures I. Genetic variation in the human insulin gene. Science. 1980;209:612–615. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information

