Development of Dictyostelium discoideum is associated with alteration of fucosylated N-glycan structures
- PMID: 19614564
- PMCID: PMC2851138
- DOI: 10.1042/BJ20090786
Development of Dictyostelium discoideum is associated with alteration of fucosylated N-glycan structures
Abstract
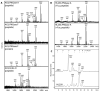
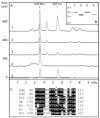
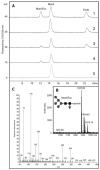
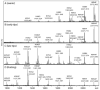
The social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum has become established as a simple model for the examination of cell-cell interactions, and early studies suggested that shifts in glycosylation profiles take place during its life cycle. In the present study, we have applied HPLC and mass spectrometric methods to show that the major N-glycans in axenic cultures of the AX3 strain are oligomannosidic forms, most of which carry core fucose and/or intersecting and bisecting N-acetylglucosamine residues, including the major structure with the composition Man8GlcNAc4Fuc1. The postulated alpha1,3-linkage of the core fucose correlates with the cross-reactivity of Dictyostelium glycoproteins with a horseradish peroxidase antiserum; a corresponding core alpha1,3-fucosyltransferase activity capable of modifying oligomannosidic N-glycans was detected in axenic Dictyostelium extracts. The presence of fucose on the N-glycans and the reactivity to the antiserum, but not the fucosyltransferase activity, are abolished in the fucose-deficient HL250 strain. In later stages of development, N-glycans at the mound and culmination stages show a reduction in both the size and the degree of modification by intersecting/bisecting residues compared with mid-exponential phase cultures, consistent with the hypothesis that glycosidase and glycosyltransferase expression levels are altered during the slime mould life cycle.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fucosebeta-1-P-Ser is a new type of glycosylation: using antibodies to identify a novel structure in Dictyostelium discoideum and study multiple types of fucosylation during growth and development.Glycobiology. 1998 Aug;8(8):799-811. doi: 10.1093/glycob/8.8.799. Glycobiology. 1998. PMID: 9639541
-
Identification of core alpha 1,3-fucosylated glycans and cloning of the requisite fucosyltransferase cDNA from Drosophila melanogaster. Potential basis of the neural anti-horseadish peroxidase epitope.J Biol Chem. 2001 Jul 27;276(30):28058-67. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M100573200. Epub 2001 May 29. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11382750
-
Discovery and structural characterization of fucosylated oligomannosidic N-glycans in mushrooms.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):5977-84. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.191304. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21169363 Free PMC article.
-
Core fucose and bisecting GlcNAc, the direct modifiers of the N-glycan core: their functions and target proteins.Carbohydr Res. 2009 Aug 17;344(12):1387-90. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2009.04.031. Epub 2009 May 4. Carbohydr Res. 2009. PMID: 19508951 Review.
-
Fucose in N-glycans: from plant to man.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999 Dec 6;1473(1):216-36. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(99)00181-6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999. PMID: 10580141 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolutionary diversity of social amoebae N-glycomes may support interspecific autonomy.Glycoconj J. 2015 Aug;32(6):345-59. doi: 10.1007/s10719-015-9592-8. Epub 2015 May 19. Glycoconj J. 2015. PMID: 25987342 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrophilic interaction anion exchange for separation of multiply modified neutral and anionic Dictyostelium N-glycans.Electrophoresis. 2017 Sep;38(17):2175-2183. doi: 10.1002/elps.201700073. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Electrophoresis. 2017. PMID: 28556908 Free PMC article.
-
Complicated N-linked glycans in simple organisms.Biol Chem. 2012 Aug;393(8):661-73. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2012-0150. Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22944671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The fucomic potential of mosquitoes: Fucosylated N-glycan epitopes and their cognate fucosyltransferases.Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016 Jan;68:52-63. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.11.001. Epub 2015 Nov 23. Insect Biochem Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26617287 Free PMC article.
-
N-glycomic and N-glycoproteomic studies in the social amoebae.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;983:205-29. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-302-2_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23494309 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Devreotes P. Dictyostelium discoideum: a model system for cell-cell interactions in development. Science. 1989;245:1054–1058. - PubMed
-
- Frazier WA, Rosen SD, Reitherman RW, Barondes SH. Purification and comparison of two developmentally regulated lectins from Dictyostelium discoideum. Discoidin I and II. J Biol Chem. 1975;250:7714–7721. - PubMed
-
- Ivatt RL, Das OP, Henderson EJ, Robbins PW. Glycoprotein biosynthesis in Dictyostelium discoideum: developmental regulation of the protein-linked glycans. Cell. 1984;38:561–567. - PubMed
-
- Tschursin E, Riley GR, Henderson EJ. Differential regulation of glycoprotein sulfation and fucosylation during growth of Dictyostelium discoideum. Differentiation. 1989;40:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

