Inactivation of astroglial NF-kappa B promotes survival of retinal neurons following ischemic injury
- PMID: 19614983
- PMCID: PMC2778328
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06814.x
Inactivation of astroglial NF-kappa B promotes survival of retinal neurons following ischemic injury
Abstract
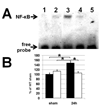
Reactive astrocytes have been implicated in neuronal loss following ischemic stroke. However, the molecular mechanisms associated with this process are yet to be fully elucidated. In this work, we tested the hypothesis that astroglial NF-kappaB, a key regulator of inflammatory responses, is a contributor to neuronal death following ischemic injury. We compared neuronal survival in the ganglion cell layer (GCL) after retinal ischemia-reperfusion in wild-type (WT) and in GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn transgenic mice, where the NF-kappaB classical pathway is suppressed specifically in astrocytes. The GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn mice showed significantly increased survival of neurons in the GCL following ischemic injury as compared with WT littermates. Neuroprotection was associated with significantly reduced expression of pro-inflammatory genes, encoding Tnf-alpha, Ccl2 (Mcp1), Cxcl10 (IP10), Icam1, Vcam1, several subunits of NADPH oxidase and NO-synthase in the retinas of GFAP-IkappaBalpha-dn mice. These data suggest that certain NF-kappaB-regulated pro-inflammatory and redox-active pathways are central to glial neurotoxicity induced by ischemic injury. The inhibition of these pathways in astrocytes may represent a feasible neuroprotective strategy for retinal ischemia and stroke.
Figures
 - GFAP-IκBα-dn sham operated,
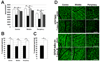
- GFAP-IκBα-dn sham operated,  - GFAP-IκBα-dn 7 days after IR injury) B. Percentage of GCL neurons lost at one week following IR of wild type and GFAP-IκBα-dn mice. Central, middle and peripheral regions were compared bilaterally for individual animals. (■ - wild type, □ - GFAP-IκBα-dn mice) C. In contrast to protected GFAP-IκBα-dn post-ischemic retinas that have lost an average of 9.6% of cells, neuronal density decreased significantly (37.5%, p<0.002) in WT ischemic retinas 7 days after reperfusion. D. Representative confocal images of NeuN-labeled GCLs (green) in flat-mounted retinas acquired at centre, middle and periphery from optic nerve in sham-operated controls and ischemic retinas 7 days after reperfusion.
- GFAP-IκBα-dn 7 days after IR injury) B. Percentage of GCL neurons lost at one week following IR of wild type and GFAP-IκBα-dn mice. Central, middle and peripheral regions were compared bilaterally for individual animals. (■ - wild type, □ - GFAP-IκBα-dn mice) C. In contrast to protected GFAP-IκBα-dn post-ischemic retinas that have lost an average of 9.6% of cells, neuronal density decreased significantly (37.5%, p<0.002) in WT ischemic retinas 7 days after reperfusion. D. Representative confocal images of NeuN-labeled GCLs (green) in flat-mounted retinas acquired at centre, middle and periphery from optic nerve in sham-operated controls and ischemic retinas 7 days after reperfusion.

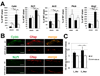
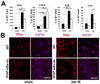
Comment in
-
Is NF-kappa B from astrocytes a decision maker of neuronal life or death? (Commentary on Dvoriantchikova et al.).Eur J Neurosci. 2009 Jul;30(2):173-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06853.x. Epub 2009 Jul 15. Eur J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19614977 Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Babior BM. NADPH oxidase: an update. Blood. 1999;93(5):1464–1476. - PubMed
-
- Bishop GM, Dringen R, et al. Zinc stimulates the production of toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inhibits glutathione reductase in astrocytes. Free Radic Biol Med. 2007;42(8):1222–1230. - PubMed
-
- Boche D, Cunningham C, et al. TGFbeta1 regulates the inflammatory response during chronic neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis. 2006;22(3):638–650. - PubMed
-
- Bracchi-Ricard V, Brambilla R, et al. Astroglial nuclear factor-kappaB regulates learning and memory and synaptic plasticity in female mice. J Neurochem. 2008;104(3):611–623. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

