Bronchoalveoloar lavage fluid cytokines and chemokines as markers and predictors for the outcome of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis patients
- PMID: 19615053
- PMCID: PMC2745793
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2766
Bronchoalveoloar lavage fluid cytokines and chemokines as markers and predictors for the outcome of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis patients
Abstract
Introduction: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a frequent manifestation of systemic sclerosis (SSc), and cytokines can contribute to the disease pathology. The aim of the current study was to identify specific changes in cytokine levels that may serve as disease markers and possible targets for therapy.
Methods: Cytokines were measured with bioplex analysis in 38 bronchoalveolar fluids (BALFs) from 32 SSc patients (27 with alveolitis and 11 without alveolitis) and 26 control patients. In the case of SSc patients, cytokines were correlated with the respective bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell differentiation, lung function, and thoracic HR-CT score. For 35 BALF samples derived from 29 SSc patients, follow-up investigations of clinical data, lung-function parameter, or thoracic HR-CT scans were available to evaluate the predictive capacity of BALF cytokines and chemokines.
Results: High IL-7 levels were characteristic of SSc-associated interstitial lung disease (ILD) and, in addition, when compared with ILD-negative SSc patients, ILD-positive SSc patients revealed higher IL-4, IL-6, IL-8, and CCL2 (MCP-1) BALF levels. High CCL2 and IL-8 BALF concentrations were associated with neutrophilic and mixed alveolitis. Cytokine levels of IL-4, IL-8, and CCL2 correlated negatively with lung-function parameters; CCL2 concentrations also correlated with HR-CT scores. High concentrations of several cytokines were associated with the progress of ILD and end-stage ILD. Univariate analyses revealed high IL-2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) levels as the best predictors for progressive disease, together with lung-function parameters, young age, and neutrophilic alveolitis. Multivariate analyses partially confirmed these results but did not sufficiently converge because of the limited number of patients.
Conclusions: The association of BALF cytokines with lung fibrosis and its progress suggests that cytokines contribute to the pathogenesis of ILD and hence could be regarded as potential therapeutic targets.
Figures
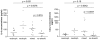
Similar articles
-
BAL cytokine profile in different interstitial lung diseases: a focus on systemic sclerosis.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004 Jun;21(2):111-8. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004. PMID: 15281432
-
CXCL11 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and pulmonary function decline in systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012 Mar-Apr;30(2 Suppl 71):S71-5. Epub 2012 May 29. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012. PMID: 22691213
-
Association of elevated α-defensin levels with interstitial pneumonia in patients with systemic sclerosis.Respir Res. 2015 Dec 10;16:148. doi: 10.1186/s12931-015-0308-1. Respir Res. 2015. PMID: 26654954 Free PMC article.
-
Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in scleroderma interstitial lung disease: technical aspects and clinical correlations: review of the literature.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010 Aug;40(1):73-88. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2008.10.009. Epub 2009 Jan 18. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010. PMID: 19152959 Review.
-
Mediators of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD): systematic review and meta-analyses.Thorax. 2023 Aug;78(8):799-807. doi: 10.1136/thorax-2022-219226. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Thorax. 2023. PMID: 36261273 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Molecular Mechanisms of Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Lung Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 3;24(3):2963. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032963. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36769282 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increased frequencies of circulating CXCL10-, CXCL8- and CCL4-producing monocytes and Siglec-3-expressing myeloid dendritic cells in systemic sclerosis patients.Inflamm Res. 2018 Feb;67(2):169-177. doi: 10.1007/s00011-017-1106-7. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Inflamm Res. 2018. PMID: 29127442 Free PMC article.
-
Serum TARC Levels in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis: Clinical Association with Interstitial Lung Disease.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 9;10(4):660. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040660. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33572144 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Biomarkers in Systemic Sclerosis: A Literature Review and Update.J Clin Med. 2020 Oct 22;9(11):3388. doi: 10.3390/jcm9113388. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33105647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serum cytokines and their predictive value in pulmonary involvement of systemic sclerosis.Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019;36(4):274-284. doi: 10.36141/svdld.v36i4.7612. Epub 2019 May 1. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2019. PMID: 32476963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Meloni F, Caporali R, Marone Bianco A, Paschetto E, Morosini M, Fietta AM, Patrizio V, Bobbio-Pallavicini F, Pozzi E, Montecucco C. BAL cytokine profile in different interstitial lung diseases: a focus on systemic sclerosis. Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis. 2004;21:111–118. - PubMed
-
- Goh NS, Veeraraghavan S, Desai SR, Cramer D, Hansell DM, Denton CP, Black CM, du Bois RM, Wells AU. Bronchoalveolar lavage cellular profiles in patients with systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease are not predictive of disease progression. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2005–2012. doi: 10.1002/art.22696. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Strange C, Bolster MB, Roth MD, Silver RM, Theodore A, Goldin J, Clements P, Chung J, Elashoff RM, Suh R, Smith AE, Furst DE, Tashkin DP, Scleroderma Lung Study Research Group Bronchoalveolar lavage and response to cyclophosphamide in scleroderma interstitial lung disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;177:91–98. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200705-655OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

