Defining the human deubiquitinating enzyme interaction landscape
- PMID: 19615732
- PMCID: PMC2716422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.042
Defining the human deubiquitinating enzyme interaction landscape
Abstract
Deubiquitinating enzymes (Dubs) function to remove covalently attached ubiquitin from proteins, thereby controlling substrate activity and/or abundance. For most Dubs, their functions, targets, and regulation are poorly understood. To systematically investigate Dub function, we initiated a global proteomic analysis of Dubs and their associated protein complexes. This was accomplished through the development of a software platform called CompPASS, which uses unbiased metrics to assign confidence measurements to interactions from parallel nonreciprocal proteomic data sets. We identified 774 candidate interacting proteins associated with 75 Dubs. Using Gene Ontology, interactome topology classification, subcellular localization, and functional studies, we link Dubs to diverse processes, including protein turnover, transcription, RNA processing, DNA damage, and endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation. This work provides the first glimpse into the Dub interaction landscape, places previously unstudied Dubs within putative biological pathways, and identifies previously unknown interactions and protein complexes involved in this increasingly important arm of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Figures



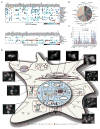

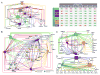

Comment in
-
Navigating the deubiquitinating proteome with a CompPASS.Cell. 2009 Jul 23;138(2):222-4. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.07.008. Cell. 2009. PMID: 19632171
References
-
- Bennett EJ, Bence NF, Jayakumar R, Kopito RR. Global impairment of the ubiquitin-proteasome system by nuclear or cytoplasmic protein aggregates precedes inclusion body formation. Mol Cell. 2005;17:351–365. - PubMed
-
- Cohn MA, Kowal P, Yang K, Haas W, Huang TT, Gygi SP, D’Andrea AD. A UAF1-containing multisubunit protein complex regulates the Fanconi anemia pathway. Mol Cell. 2007;28:786–797. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

