In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia
- PMID: 19616412
- PMCID: PMC2862048
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2009.06.014
In vivo evidence of differential impact of typical and atypical antipsychotics on intracortical myelin in adults with schizophrenia
Abstract
Context: Imaging and post-mortem studies provide converging evidence that patients with schizophrenia have a dysregulated developmental trajectory of frontal lobe myelination. The hypothesis that typical and atypical medications may differentially impact brain myelination in adults with schizophrenia was previously assessed with inversion recovery (IR) images. Increased white matter (WM) volume suggestive of increased myelination was detected in the patient group treated with an atypical antipsychotic compared to a typical one.
Objective: In a follow-up reanalysis of MRI images from the original study, we used a novel method to assess whether the difference in WM volumes could be caused by a differential effect of medications on the intracortical myelination process.
Design, setting, and participants: Two different male cohorts of healthy controls ranging in age from 18-35 years were compared to cohorts of subjects with schizophrenia who were treated with either oral risperidone (Ris) or fluphenazine decanoate (Fd).
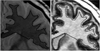
Main outcome measure: A novel MRI method that combines the distinct tissue contrasts provided by IR and proton density (PD) images was used to estimate intracortical myelin (ICM) volume.
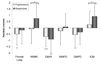
Results: When compared with their pooled healthy control comparison group, the two groups of schizophrenic patients differed in the frontal lobe ICM measure with the Ris group having significantly higher volume.
Conclusions: The data suggest that in adults with schizophrenia antipsychotic treatment choice may be specifically and differentially impacting later-myelinating intracortical circuitry. In vivo MRI can be used to dissect subtle differences in brain tissue characteristics and thus help clarify the effect of pharmacologic treatments on developmental and pathologic processes.
Figures
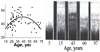
References
-
- Allen JS, Bruss J, Brown CK, Damasio H. Normal neuroanatomical variation due to age: The major lobes and a parcellation of the temporal region. Neurobiol Aging. 2005;26:1245–1260. - PubMed
-
- Altar CA, Hunt RA, Jurata LW, Webster MJ, Derby E, Gallagher P, et al. Insulin, IGF-1, and muscarinic agonists modulate schizophrenia-associated genes in human neuroblastoma cells. Biol Psychiatry. 2008;64:1077–1087. - PubMed
-
- Aston C, Jiang L, Sokolov BP. Microarray analysis of postmortem temporal cortex from patients with schizophrenia. J Neurosci Res. 2004;77:858–866. - PubMed
-
- Aston C, Jiang L, Sokolov BP. Transcriptional profiling reveals evidence for signaling and oligodendroglial abnormalities in the temporal cortex from patients with major depressive disorder. Mol Psychiatry. 2005;10:309–322. - PubMed
-
- Aznavour N, Watkins KC, Descarries L. Postnatal development of the cholinergic innervation in the dorsal hippocampus of rat: Quantitative light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol. 2005;486:61–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

