Highly cooperative recruitment of Ets-1 and release of autoinhibition by Pax5
- PMID: 19616560
- PMCID: PMC2763353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.07.028
Highly cooperative recruitment of Ets-1 and release of autoinhibition by Pax5
Abstract
Pax5 (paired box binding factor 5) is a critical regulator of transcription and lineage commitment in B lymphocytes. In B cells, mb-1 (Ig-alpha/immunoglobulin-associated alpha) promoter transcription is activated by Pax5 through its recruitment of E74-like transforming sequence (Ets) family proteins to a composite site, the P5-EBS (Pax5-Ets binding site). Previously, X-ray crystallographic analysis revealed a network of contacts between the DNA-binding domains of Pax5 and Ets-1 while bound to the P5-EBS. Here, we report that Pax5 assembles these ternary complexes via highly cooperative interactions that overcome the autoinhibition of Ets-1. Using recombinant proteins, we calculated K(d(app)) values for the binding of Pax5, Ets-1, and GA-binding proteins, separately or together, to the P5-EBS. By itself, Pax5 binds the P5-EBS with high affinity (K(d) approximately equal 2 nM). Ets-1(331-440) bound the P5-EBS by itself with low affinity (K(d)=136 nM). However, autoinhibited Ets-1(280-440) alone does not bind detectably to the suboptimal sequences of the P5-EBS. Recruitment of Ets-1(331-440) or Ets-1(280-440) resulted in highly efficient ternary complex assembly with Pax5. Pax5 counteracts autoinhibition and increases binding of Ets-1 of the mb-1 promoter by >1000-fold. Mutation of Pax5 Gln22 to alanine (Q22A) enhances promoter binding by Pax5; however, Q22A greatly reduces recruitment of Ets-1(331-440) and Ets-1(280-440) by Pax5 (8.9- or >300-fold, respectively). Thus, Gln22 of Pax5 is essential for overcoming Ets-1 autoinhibition. Pax5 wild type and Q22A each recruited GA-binding protein alpha/beta1 to the mb-1 promoter with similar affinities, but recruitment was less efficient than that of Ets-1 (reduced by approximately 8-fold). Our results suggest a mechanism that allows Pax5 to overcome autoinhibition of Ets-1 DNA binding. In summary, these data illustrate requirements for partnerships between Ets proteins and Pax5.
Figures

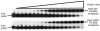
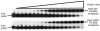














Similar articles
-
Highly conserved amino acids in Pax and Ets proteins are required for DNA binding and ternary complex assembly.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Oct 15;29(20):4154-65. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.20.4154. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11600704 Free PMC article.
-
Requirements for selective recruitment of Ets proteins and activation of mb-1/Ig-alpha gene transcription by Pax-5 (BSAP).Nucleic Acids Res. 2003 Oct 1;31(19):5483-9. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg785. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003. PMID: 14500810 Free PMC article.
-
Structural studies of Ets-1/Pax5 complex formation on DNA.Mol Cell. 2001 Dec;8(6):1267-76. doi: 10.1016/s1097-2765(01)00410-5. Mol Cell. 2001. PMID: 11779502
-
The highly conserved beta-hairpin of the paired DNA-binding domain is required for assembly of Pax-Ets ternary complexes.Mol Cell Biol. 1999 Mar;19(3):2231-41. doi: 10.1128/MCB.19.3.2231. Mol Cell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10022910 Free PMC article.
-
Ets-1 binds cooperatively to the palindromic Ets-binding sites in the p53 promoter.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009 Jan 9;378(2):213-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.11.035. Epub 2008 Nov 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009. PMID: 19022222
Cited by
-
Review of Ets1 structure, function, and roles in immunity.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Sep;70(18):3375-90. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1243-7. Epub 2013 Jan 5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 23288305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of ETS1 in the Transcriptional Network of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma of the Activated B Cell-Like Type.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jul 15;12(7):1912. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071912. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32679859 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic and biochemical insights into the specificity of ETS transcription factors.Annu Rev Biochem. 2011;80:437-71. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.79.081507.103945. Annu Rev Biochem. 2011. PMID: 21548782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ETV4 and AP1 Transcription Factors Form Multivalent Interactions with three Sites on the MED25 Activator-Interacting Domain.J Mol Biol. 2017 Oct 13;429(20):2975-2995. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.06.024. Epub 2017 Jul 17. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28728983 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of cognate sequence discrimination by the ETS-family transcription factor ETS-1.J Biol Chem. 2019 Jun 21;294(25):9666-9678. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.007866. Epub 2019 May 2. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31048376 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karim FD, Urness LD, Thummel CS, Klemsz MJ, McKercher SR, Celada A, Beveran Cv, Maki RA, Gunther CV, Nye JA, Graves BJ. The ETS-domain: a new DNA-binding motif that recognizes a purine-rich core DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990;4:1451–1453. - PubMed
-
- Thompson CC, Brown TA, McKnight SL. Convergence of ets- and notch-related structural motifs in a heteromeric DNA binding complex. Science. 1991;253:762–768. - PubMed
-
- Batchelor AH, Piper DE, de la Brousse FC, McKnight SL, Wolberger C. The structure of GABPα/β: an ETS domain-ankyrin repeat heterodimer bound to DNA. Science. 1998;279:1037–1041. - PubMed
-
- Chinenov Y, Henzl M, Martin ME. The α and β subunits of the GA-binding protein form a stable heterodimer in solution. J Biol Chem. 2000;275:7749–7756. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

