The small acid soluble proteins (SASP alpha and SASP beta) of Bacillus weihenstephanensis and Bacillus mycoides group 2 are the most distinct among the Bacillus cereus group
- PMID: 19616612
- PMCID: PMC2783214
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcp.2009.07.003
The small acid soluble proteins (SASP alpha and SASP beta) of Bacillus weihenstephanensis and Bacillus mycoides group 2 are the most distinct among the Bacillus cereus group
Abstract
The Bacillus cereus group includes Bacillus anthracis, B. cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Bacillus mycoides and Bacillus weihenstephanensis. The small acid soluble spore protein (SASP) beta has been previously demonstrated to be among the biomarkers differentiating B. anthracis and B. cereus; SASP beta of B. cereus most commonly exhibits one or two amino acid substitutions when compared to B. anthracis. SASP alpha is conserved in sequence among these two species. Neither SASP alpha nor beta for B. thuringiensis, B. mycoides and B. weihenstephanensis have been previously characterized as taxonomic discriminators. In the current work molecular weight (MW) variation of these SASPs were determined by matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for representative strains of the 5 species within the B. cereus group. The measured MWs also correlate with calculated MWs of translated amino acid sequences generated from whole genome sequencing projects. SASP alpha and beta demonstrated consistent MW among B. cereus, B. thuringiensis, and B. mycoides strains (group 1). However B. mycoides (group 2) and B. weihenstephanensis SASP alpha and beta were quite distinct making them unique among the B. cereus group. Limited sequence changes were observed in SASP alpha (at most 3 substitutions and 2 deletions) indicating it is a more conserved protein than SASP beta (up to 6 substitutions and a deletion). Another even more conserved SASP, SASP alpha-beta type, was described here for the first time.
Figures
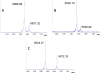
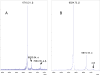
References
-
- Hoffmaster AR, Hill KK, Gee JE, Marston CK, De BK, Popovic T, Sue D, Wilkins PP, Avashia SB, Drumgoole R, Helma CH, Ticknor LO, Okinaka RT, Jackson PJ. Characterization of Bacillus cereus isolates associated with fatal pneumonias: strains are closely related to Bacillus anthracis and harbor B. anthracis virulence genes. J Clin Microbiol. 2006;44:3352–60. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lechner S, Mayr R, Francis KP, Pruβ BM, Kaplan T, Weiβner-Gunkel E, Stewart SAB, Scherer S. Bacillus weihenstephanensis sp. nov. is a new psychrotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1998;48:1373–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

