Alpha-lipoic acid induces elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine and depletes S-adenosylmethionine
- PMID: 19616616
- PMCID: PMC2782850
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.019
Alpha-lipoic acid induces elevated S-adenosylhomocysteine and depletes S-adenosylmethionine
Abstract
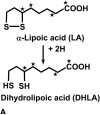
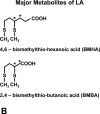
Lipoic acid is a disulfhydryl-containing compound used in clinical medicine and in experimental models as an antioxidant. We developed a stable isotope dilution capillary gas chromatography/mass spectrometry assay for lipoic acid. We assayed a panel of the metabolites of transmethylation and transsulfuration 30 min after injecting 100 mg/kg lipoic acid in a rat model. Lipoic acid values rose 1000-fold in serum and 10-fold in liver. A methylated metabolite of lipoic acid was also detected but not quantitated. Lipoic acid injection caused a massive increase in serum S-adenosylhomocysteine and marked depletion of liver S-adenosylmethionine. Serum total cysteine was depleted but liver cysteine and glutathione were maintained. Serum total homocysteine doubled, with increases also in cystathionine, N,N-dimethylglycine, and alpha-aminobutyric acid. In contrast, after injection of 2-mercaptoethane sulfonic acid, serum total cysteine and homocysteine were markedly depleted and there were no effects on serum S-adenosylmethionine or S-adenosylhomocysteine. We conclude that large doses of lipoic acid displace sulfhydryls from binding sites, resulting in depletion of serum cysteine, but also pose a methylation burden with severe depletion of liver S-adenosylmethionine and massive release of S-adenosylhomocysteine. These changes may have previously unrecognized deleterious effects that should be investigated in both human disease and experimental models.
Figures
References
-
- Ziegler D, Ametov A, Barinov A, Dyck PJ, Gurieva I, Low PA, Munzel U, Yakhno N, Raz I, Novosadova M, Maus J, Samigullin R. Oral treatment with alpha-lipoic acid improves symptomatic diabetic polyneuropathy: the SYDNEY 2 trial. Diabetes Care. 2006;29:2365–2370. - PubMed
-
- Packer L, Witt EH, Tritschler HJ. Alpha-Lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1995;19:227–250. - PubMed
-
- Lateef H, Aslam MN, Stevens MJ, Varani J. Pretreatment of diabetic rats with lipoic acid improves healing of subsequently-induced abrasion wounds. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2005;297:75–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

