Chest tomosynthesis: technical principles and clinical update
- PMID: 19616909
- PMCID: PMC3693857
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2009.05.054
Chest tomosynthesis: technical principles and clinical update
Abstract
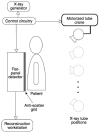
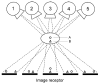
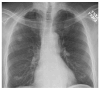
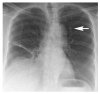
Digital tomosynthesis is a radiographic technique that can produce an arbitrary number of section images of a patient from a single pass of the X-ray tube. It utilizes a conventional X-ray tube, a flat-panel detector, a computer-controlled tube mover, and special reconstruction algorithms to produce section images. While it does not have the depth resolution of computed tomography (CT), tomosynthesis provides some of the tomographic benefits of CT but at lower cost and radiation dose than CT. Compared to conventional chest radiography, chest tomosynthesis results in improved visibility of normal structures such as vessels, airway and spine. By reducing visual clutter from overlying normal anatomy, it also enhances detection of small lung nodules. This review article outlines the components of a tomosynthesis system, discusses results regarding improved lung nodule detection from the recent literature, and presents examples of nodule detection from a clinical trial in human subjects. Possible implementation strategies for use in clinical chest imaging are discussed.
Figures







References
-
- McAdams HP, Samei E, Dobbins J, 3rd, Tourassi GD, Ravin CE. Recent advances in chest radiography. Radiology. 2006;241:663–683. - PubMed
-
- Pascoal A, Lawinski CP, Mackenzie A, Tabakov S, Lewis CA. Chest radiography: a comparison of image quality and effective dose using four digital systems. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005;114:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Ricke J, Fischbach F, Freund T, et al. Clinical results of CsI-detector-based dual-exposure dual energy in chest radiography. European Radiology. 2003;13:2577–2582. - PubMed
-
- MacMahon H, Li F, Engelmann R, Roberts R, Armato S. Dual energy subtraction and temporal subtraction chest radiography. J Thorac Imaging. 2008;23:77–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

