Secondary acylation of Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide requires phosphorylation of Kdo
- PMID: 19617350
- PMCID: PMC2757982
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.022772
Secondary acylation of Vibrio cholerae lipopolysaccharide requires phosphorylation of Kdo
Abstract
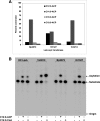
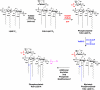
The lipopolysaccharide of Vibrio cholerae has been reported to contain a single 3-deoxy-d-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) residue that is phosphorylated. The phosphorylated Kdo sugar further links the hexa-acylated V. cholerae lipid A domain to the core oliogosaccharide and O-antigen. In this report, we confirm that V. cholerae possesses the enzymatic machinery to synthesize a phosphorylated Kdo residue. Further, we have determined that the presence of the phosphate group on the Kdo residue is necessary for secondary acylation in V. cholerae. The requirement for a secondary substituent on the Kdo residue (either an additional Kdo sugar or a phosphate group) was also found to be critical for secondary acylation catalyzed by LpxL proteins from Bordetella pertussis, Escherichia coli, and Haemophilus influenzae. Although three putative late acyltransferase orthologs have been identified in the V. cholerae genome (Vc0212, Vc0213, and Vc1577), only Vc0213 appears to be functional. Vc0213 functions as a myristoyl transferase acylating lipid A at the 2'-position of the glucosamine disaccharide. Generally acyl-ACPs serve as fatty acyl donors for the acyltransferases required for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis; however, in vitro assays indicate that Vc0213 preferentially utilizes myristoyl-CoA as an acyl donor. This is the first report to biochemically characterize enzymes involved in the biosynthesis of the V. cholerae Kdo-lipid A domain.
Figures
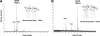
Similar articles
-
Elucidation of a novel Vibrio cholerae lipid A secondary hydroxy-acyltransferase and its role in innate immune recognition.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Sep;81(5):1313-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07765.x. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21752109 Free PMC article.
-
Biosynthesis of lipid A in Escherichia coli. Acyl carrier protein-dependent incorporation of laurate and myristate.J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15410-7. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2203778
-
Lipopolysaccharide 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) core determines bacterial association of secreted toxins.J Biol Chem. 2004 Feb 27;279(9):8070-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M308633200. Epub 2003 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14660669 Free PMC article.
-
Lipopolysaccharides of Vibrio cholerae II. Genetics of biosynthesis.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004 Oct 14;1690(2):93-109. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.06.006. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004. PMID: 15469898 Review.
-
Conservation of the 2-keto-3-deoxymanno-octulosonic acid (Kdo) biosynthesis pathway between plants and bacteria.Carbohydr Res. 2013 Oct 18;380:70-5. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2013.07.006. Epub 2013 Jul 20. Carbohydr Res. 2013. PMID: 23974348 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino acid addition to Vibrio cholerae LPS establishes a link between surface remodeling in gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 May 29;109(22):8722-7. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1201313109. Epub 2012 May 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22589301 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and chemical characterization of lipid A from gram-negative bacteria.J Vis Exp. 2013 Sep 16;(79):e50623. doi: 10.3791/50623. J Vis Exp. 2013. PMID: 24084191 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidation of a novel Vibrio cholerae lipid A secondary hydroxy-acyltransferase and its role in innate immune recognition.Mol Microbiol. 2011 Sep;81(5):1313-29. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07765.x. Epub 2011 Jul 18. Mol Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21752109 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of the outer Kdo from Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide and its impact on the bacterial surface.Mol Microbiol. 2010 Nov;78(4):837-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2010.07304.x. Mol Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20659292 Free PMC article.
-
Homeoviscous Adaptation of the Acinetobacter baumannii Outer Membrane: Alteration of Lipooligosaccharide Structure during Cold Stress.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0129521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01295-21. Epub 2021 Aug 24. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34425709 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Trent M. S., Stead C. M., Tran A. X., Hankins J. V. (2006) J. Endotoxin Res. 12, 205–223 - PubMed
-
- Meredith T. C., Aggarwal P., Mamat U., Lindner B., Woodard R. W. (2006) ACS Chem. Biol. 1, 33–42 - PubMed
-
- Clementz T., Raetz C. R. (1991) J. Biol. Chem. 266, 9687–9696 - PubMed
-
- White K. A., Kaltashov I. A., Cotter R. J., Raetz C. R. (1997) J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16555–16563 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

