Anti-VEGF single-chain antibody GLAF-1 encoded by oncolytic vaccinia virus significantly enhances antitumor therapy
- PMID: 19617539
- PMCID: PMC2722284
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0900660106
Anti-VEGF single-chain antibody GLAF-1 encoded by oncolytic vaccinia virus significantly enhances antitumor therapy
Abstract
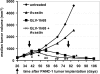
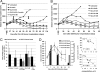
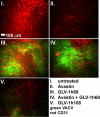
We previously reported that the replication-competent vaccinia virus (VACV) GLV-1h68 shows remarkable oncolytic activity and efficacy in different animal models as a single treatment modality and also in combination with chemotherapy [Yu YA, et al. (2009) Mol Cancer Ther 8:141-151]. Here, we report the construction of 3 VACV strains encoding GLAF-1, a previously undescribed engineered single-chain antibody (scAb). This unique scAb is transcribed from 3 vaccinia promoters (synthetic early, early/late, and late) and directed against both human and murine VEGFs. The expression of GLAF-1 was demonstrated in cell cultures. Also, the replication efficiency of all GLAF-1-expressing VACV strains in cell culture was similar to that of the parental GLV-1h68 virus. Successful tumor-specific delivery and continued production of functional scAb derived from individual VACV strains were obtained in tumor xenografts following a single intravenous injection of the virus. The VACV strains expressing the scAb exhibited significantly enhanced therapeutic efficacy in comparison to treatment of human tumor xenografts with the parental virus GLV-1h68. This enhanced efficacy was comparable to the concomitant treatment of tumors with a one-time i.v. injection of GLV-1h68 and multiple i.p. injections of Avastin. Taken together, the VACV-mediated delivery and production of immunotherapeutic anti-VEGF scAb in colonized tumors may open the way for a unique therapy concept: tumor-specific, locally amplified drug therapy in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.F., Y.A.Y., N.C., Q.Z., and A.A.S. are employees of Genelux Corporation.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2008. Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008.
-
- Jain RK. Delivery of novel therapeutic agents in tumors: Physiological barriers and strategies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1989;81:570–576. - PubMed
-
- Jain RK. Delivery of molecular and cellular medicine to solid tumors. Adv Drug Delivery Rev. 2001;46:149–168. - PubMed
-
- Reilly RM, et al. Problems of delivery of monoclonal antibodies. Pharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic solutions. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1995;28:126–142. - PubMed
-
- Manegold C. Bevacizumab for the treatment of advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008;8:689–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

