Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening
- PMID: 19617544
- PMCID: PMC2732882
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903542106
Droplet microfluidic technology for single-cell high-throughput screening
Abstract
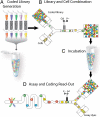
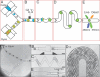
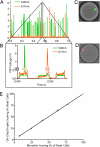
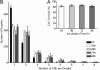
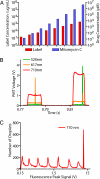
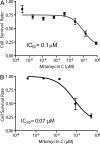
We present a droplet-based microfluidic technology that enables high-throughput screening of single mammalian cells. This integrated platform allows for the encapsulation of single cells and reagents in independent aqueous microdroplets (1 pL to 10 nL volumes) dispersed in an immiscible carrier oil and enables the digital manipulation of these reactors at a very high-throughput. Here, we validate a full droplet screening workflow by conducting a droplet-based cytotoxicity screen. To perform this screen, we first developed a droplet viability assay that permits the quantitative scoring of cell viability and growth within intact droplets. Next, we demonstrated the high viability of encapsulated human monocytic U937 cells over a period of 4 days. Finally, we developed an optically-coded droplet library enabling the identification of the droplets composition during the assay read-out. Using the integrated droplet technology, we screened a drug library for its cytotoxic effect against U937 cells. Taken together our droplet microfluidic platform is modular, robust, uses no moving parts, and has a wide range of potential applications including high-throughput single-cell analyses, combinatorial screening, and facilitating small sample analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Unger MA, et al. Monolithic microfabricated valves and pumps by multilayer soft lithography. Science. 2000;288:113–116. - PubMed
-
- Clausell-Tormos J, et al. Droplet-based microfluidic platforms for the encapsulation and screening of Mammalian cells and multicellular organisms. Chem Biol. 2008;15:427–437. - PubMed
-
- He M, et al. Selective encapsulation of single cells and subcellular organelles into picoliter- and femtoliter-volume droplets. Anal Chem. 2005;77:1539–1544. - PubMed
-
- Huebner A, et al. Quantitative detection of protein expression in single cells using droplet microfluidics. Chem Commun. 2007;12:1218–1220. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

