TCR-inducible PLZF transcription factor required for innate phenotype of a subset of gammadelta T cells with restricted TCR diversity
- PMID: 19617548
- PMCID: PMC2718370
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903895106
TCR-inducible PLZF transcription factor required for innate phenotype of a subset of gammadelta T cells with restricted TCR diversity
Abstract
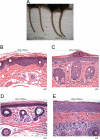
Some gammadelta and alphabeta T lymphocytes exhibit an "innate" phenotype associated with rapid cytokine responses. The PLZF transcription factor is essential for the innate phenotype of NKT cells. This report shows that PLZF is likewise responsible for the innate, NKT-like phenotype of Vgamma1+Vdelta6.3/Vdelta6.4+ cells. TCR cross-linking induced PLZF expression in all polyclonal immature gammadelta thymocytes, suggesting that agonist selection might be required for PLZF induction. Transgenic expression of Vgamma1Vdelta6.4 TCR was sufficient to support the development of large numbers of PLZF+ T cells, further supporting the importance of the TCR for PLZF induction. Interestingly, expression of this TCR transgene led to the development of spontaneous dermatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Berg LJ. Signalling through TEC kinases regulates conventional versus innate CD8(+) T-cell development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Jameson J, Witherden D, Havran WL. T-cell effector mechanisms: Gammadelta and CD1d-restricted subsets. Curr Opin Immunol. 2003;15:349–353. - PubMed
-
- Hayday AC. γδ cells: A right time and a right place for a conserved third way of protection. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:975–1026. - PubMed
-
- Hayday A, Tigelaar R. Immunoregulation in the tissues by γδ T cells. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:233–242. - PubMed
-
- Eberl G, Littman DR. Thymic origin of intestinal αβ T cells revealed by fate mapping of RORγt+ cells. Science. 2004;305:248–251. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

