Calpain-1 cleaves and activates caspase-7
- PMID: 19617626
- PMCID: PMC2757245
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.038174
Calpain-1 cleaves and activates caspase-7
Abstract
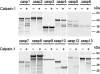
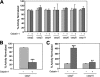
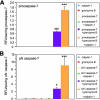
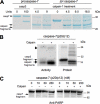
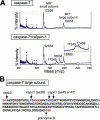
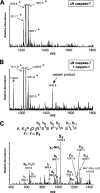
Caspase-7 is an executioner caspase that plays a key role in apoptosis, cancer, and a number of neurodegenerative diseases. The mechanism of caspase-7 activation by granzyme B and caspase-3 has been well characterized. However, whether other proteases such as calpains activate or inactivate caspase-7 is not known. Here, we present that recombinant caspase-7 is directly cleaved by calpain-1 within the large subunit of caspase-7 to produce two novel products, large subunit p18 and p17. This new form of caspase-7 has a 6-fold increase in V(max) when compared with the previously characterized p20/p12 form. Zymography revealed that the smaller caspase-7 product (p17) is 18-fold more active than either the caspase-3-cleaved product (p20) or the larger calpain-1 product of caspase-7 (p18). Mass spectrometry and site-directed mutagenesis identified the calpain cleavage sites within the caspase-7 large subunit at amino acid 36 and 45/47. These proteolysis events occur in vivo as indicated by the accumulation of caspase-7 p18 and p17 subunits in cortical neurons undergoing Ca(2+) dysregulation. Further, cleavage at amino acid 45/47 of caspase-7 by calpain results in a reduction in nuclear localization when compared with the caspase-3 cleavage product of caspase-7 (p20). Our studies suggest the calpain-activated form of caspase-7 has unique enzymatic activity, localization, and binding affinity when compared with the caspase-activated form.
Figures



Similar articles
-
In vivo calpain/caspase cross-talk during 3-nitropropionic acid-induced striatal degeneration: implication of a calpain-mediated cleavage of active caspase-3.J Biol Chem. 2003 Oct 31;278(44):43245-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305057200. Epub 2003 Aug 12. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12917435
-
Inhibition of calpain cleavage of huntingtin reduces toxicity: accumulation of calpain/caspase fragments in the nucleus.J Biol Chem. 2004 May 7;279(19):20211-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401267200. Epub 2004 Feb 23. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14981075
-
Direct cleavage by the calcium-activated protease calpain can lead to inactivation of caspases.J Biol Chem. 2000 Feb 18;275(7):5131-5. doi: 10.1074/jbc.275.7.5131. J Biol Chem. 2000. PMID: 10671558
-
Predictions of Cleavability of Calpain Proteolysis by Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Analysis Using Newly Determined Cleavage Sites and Catalytic Efficiencies of an Oligopeptide Array.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016 Apr;15(4):1262-80. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M115.053413. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26796116 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium signaling in cancer and vitamin D.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 Oct;97(1-2):145-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.06.007. Epub 2005 Aug 2. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 16081284 Review.
Cited by
-
The calpain system as a potential target for pelvic muscle reinforcement.Cent European J Urol. 2011;64(3):128-33. doi: 10.5173/ceju.2011.03.art4. Epub 2011 Sep 6. Cent European J Urol. 2011. PMID: 24578879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin Anti-Apoptotic Potential Mediates Neuroprotection Against 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Huntington's Disease-Like Pathophysiology in Rats: Involvement of Calpain-2/p25 Cdk5/MEF-2 Signaling Pathway.Neurochem Res. 2025 Apr 19;50(3):148. doi: 10.1007/s11064-025-04397-9. Neurochem Res. 2025. PMID: 40252127
-
TNFα induces Ca2+ influx to accelerate extrinsic apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 5;37(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0714-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29506556 Free PMC article.
-
Calpain1 inhibition enhances autophagy-lysosomal pathway and ameliorates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in Nephronophthisis.Mol Med. 2025 May 3;31(1):166. doi: 10.1186/s10020-025-01231-4. Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40319239 Free PMC article.
-
The role of calcium-calpain pathway in hyperthermia.Front Mol Med. 2022 Oct 10;2:1005258. doi: 10.3389/fmmed.2022.1005258. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 39086981 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

