Dioxin receptor deficiency impairs angiogenesis by a mechanism involving VEGF-A depletion in the endothelium and transforming growth factor-beta overexpression in the stroma
- PMID: 19617630
- PMCID: PMC2757217
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.013292
Dioxin receptor deficiency impairs angiogenesis by a mechanism involving VEGF-A depletion in the endothelium and transforming growth factor-beta overexpression in the stroma
Abstract
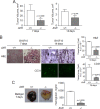
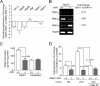
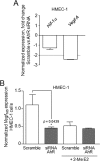
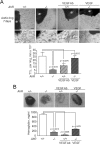
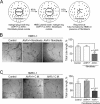
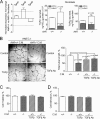
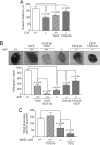
Angiogenesis has key roles in development and in the progression of human diseases such as cancer. Consequently, identifying the novel markers and regulators of angiogenesis is a critical task. The dioxin receptor (AhR) contributes to vascular homeostasis and to the endothelial response to toxins, although the mechanisms involved are largely uncharacterized. Here, we show that AhR-null mice (AhR(-/-)) have impaired angiogenesis in vivo that compromises tumor xenograft growth. Aortic rings emigration experiments and RNA interference indicated that AhR(-/-) endothelial cells failed to branch and to form tube-like structures. Such a phenotype was found to be vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-dependent, as AhR(-/-) aortic endothelial cells (MAECs) secreted lower amounts of active VEGF-A and their treatment with VEGF-A rescued angiogenesis in culture and in vivo. Further, the addition of anti-VEGF antibody to AhR(+/+) MAECs reduced angiogenesis. Treatment under hypoxic conditions with 2-methoxyestradiol suggested that HIF-1alpha modulates endothelial VEGF expression in an AhR-dependent manner. Importantly, AhR-null stromal myofibroblasts produced increased transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) activity, which inhibited angiogenesis in human endothelial cells (HMECs) and AhR(-/-) mice, whereas the co-culture of HMECs with AhR(-/-) myofibroblasts or with their conditioned medium inhibited branching, which was restored by an anti-TGFbeta antibody. Moreover, VEGF and TGFbeta activities cooperated in modulating angiogenesis, as the addition of TGFbeta to AhR(-/-) MAECs further reduced their low basal VEGF-A activity. Thus, AhR modulates angiogenesis through a mechanism requiring VEGF activation in the endothelium and TGFbeta inactivation in the stroma. These data highlight the role of AhR in cardiovascular homeostasis and suggest that this receptor can be a novel regulator of angiogenesis during tumor development.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) inhibits vanadate-induced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) production in TRAMP prostates.Carcinogenesis. 2008 May;29(5):1077-82. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgn069. Epub 2008 Mar 20. Carcinogenesis. 2008. PMID: 18359762 Free PMC article.
-
Aromatic hydrocarbon receptor inhibits lysophosphatidic acid-induced vascular endothelial growth factor-A expression in PC-3 prostate cancer cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Aug 2;437(3):440-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.06.098. Epub 2013 Jul 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23831623
-
Aromatic Hydrocarbon Receptor Suppresses Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Cells-Induced Vasculogenesis of Endothelial Progenitor Cells under Hypoxia.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;39(2):709-20. doi: 10.1159/000445662. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27448695
-
Fitting a xenobiotic receptor into cell homeostasis: how the dioxin receptor interacts with TGFbeta signaling.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Feb 15;77(4):700-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2008.08.032. Epub 2008 Sep 5. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 18812170 Review.
-
Dual Roles of the AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Pathway in Angiogenesis.Cells. 2019 Jul 19;8(7):752. doi: 10.3390/cells8070752. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31331111 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and lung cancer.Anticancer Res. 2013 Apr;33(4):1247-56. Anticancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23564762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dioxin receptor regulates aldehyde dehydrogenase to block melanoma tumorigenesis and metastasis.Mol Cancer. 2015 Aug 5;14:148. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0419-9. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26242870 Free PMC article.
-
Lung cancer associated with combustion particles and fine particulate matter (PM2.5) - The roles of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR).Biochem Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;216:115801. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115801. Epub 2023 Sep 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37696458 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dioxin receptor and SLUG transcription factors regulate the insulator activity of B1 SINE retrotransposons via an RNA polymerase switch.Genome Res. 2011 Mar;21(3):422-32. doi: 10.1101/gr.111203.110. Epub 2011 Feb 3. Genome Res. 2011. PMID: 21324874 Free PMC article.
-
High Expression of AhR and Environmental Pollution as AhR-Linked Ligands Impact on Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in Western Patients with Gastric Cancer-A Pilot Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Aug 20;12(8):1905. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081905. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200369 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd R. V., Vidal S., Horvath E., Kovacs K., Scheithauer B. (2003) Microsc. Res. Tech. 60, 244–250 - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N., Alitalo K. (1999) Nat. Med. 5, 1359–1364 - PubMed
-
- Tammela T., Zarkada G., Wallgard E., Murtomäki A., Suchting S., Wirzenius M., Waltari M., Hellström M., Schomber T., Peltonen R., Freitas C., Duarte A., Isoniemi H., Laakkonen P., Christofori G., Ylä-Herttuala S., Shibuya M., Pytowski B., Eichmann A., Betsholtz C., Alitalo K. (2008) Nature 454, 656–660 - PubMed
-
- Childs S., Chen J. N., Garrity D. M., Fishman M. C. (2002) Development 129, 973–982 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

