Dysbindin-1 in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia cases is reduced in an isoform-specific manner unrelated to dysbindin-1 mRNA expression
- PMID: 19617633
- PMCID: PMC2748893
- DOI: 10.1093/hmg/ddp329
Dysbindin-1 in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia cases is reduced in an isoform-specific manner unrelated to dysbindin-1 mRNA expression
Abstract
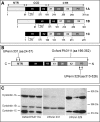
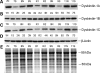
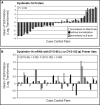
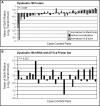
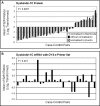
DTNBP1 (dystrobrevin binding protein 1) remains a top candidate gene in schizophrenia. Reduced expression of this gene and of its encoded protein, dysbindin-1, have been reported in the brains of schizophrenia cases. It has not been established, however, if the protein reductions encompass all dysbindin-1 isoforms or if they are associated with decreased DTNBP1 gene expression. Using a matched pairs design in which each of 28 Caucasian schizophrenia cases was matched in age and sex to a normal Caucasian control, Western blotting of whole-tissue lysates of dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) revealed significant reductions in dysbindin-1C (but not in dysbindin-1A or -1B) in schizophrenia (P = 0.022). These reductions occurred without any significant change in levels of the encoding transcript in the same tissue samples and in the absence of the only DTNBP1 risk haplotype for schizophrenia reported in the USA. Indeed, no significant correlations were found between case-control differences in any dysbindin-1 isoform and the case-control differences in its encoding mRNA. Consequently, the mean 60% decrease in dysbindin-1C observed in 71% of our case-control pairs appears to reflect abnormalities in mRNA translation and/or processes promoting dysbindin-1C degradation (e.g. oxidative stress, phosphorylation and/or ubiquitination). Given the predominantly post-synaptic localization of dysbindin-1C and known post-synaptic effects of dysbindin-1 reductions in the rodent equivalent of the DLPFC, the present findings suggest that decreased dysbindin-1C in the DLPFC may contribute to the cognitive deficits of schizophrenia by promoting NMDA receptor hypofunction in fast-spiking interneurons.
Figures

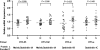
Similar articles
-
Synaptic dysbindin-1 reductions in schizophrenia occur in an isoform-specific manner indicating their subsynaptic location.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 1;6(3):e16886. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016886. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21390302 Free PMC article.
-
Human dysbindin (DTNBP1) gene expression in normal brain and in schizophrenic prefrontal cortex and midbrain.Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004 Jun;61(6):544-55. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.61.6.544. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2004. PMID: 15184234
-
Lack of change in markers of presynaptic terminal abundance alongside subtle reductions in markers of presynaptic terminal plasticity in prefrontal cortex of schizophrenia patients.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Jan 1;69(1):71-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.036. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21145444 Free PMC article.
-
Developmental Genes and Regulatory Proteins, Domains of Cognitive Impairment in Schizophrenia Spectrum Psychosis and Implications for Antipsychotic Drug Discovery: The Example of Dysbindin-1 Isoforms and Beyond.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jan 29;10:1638. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.01638. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32063853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is the dysbindin gene (DTNBP1) a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia?Schizophr Bull. 2005 Oct;31(4):800-5. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbi061. Epub 2005 Sep 15. Schizophr Bull. 2005. PMID: 16166606 Review.
Cited by
-
The Endosome Localized Arf-GAP AGAP1 Modulates Dendritic Spine Morphology Downstream of the Neurodevelopmental Disorder Factor Dysbindin.Front Cell Neurosci. 2016 Sep 22;10:218. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2016.00218. eCollection 2016. Front Cell Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27713690 Free PMC article.
-
The schizophrenia susceptibility factor dysbindin and its associated complex sort cargoes from cell bodies to the synapse.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Dec;22(24):4854-67. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E11-07-0592. Epub 2011 Oct 12. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21998198 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal copper homeostasis susceptibility by genetic defects in dysbindin, a schizophrenia susceptibility factor.Hum Mol Genet. 2015 Oct 1;24(19):5512-23. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddv282. Epub 2015 Jul 21. Hum Mol Genet. 2015. PMID: 26199316 Free PMC article.
-
A polymorphism in the dysbindin gene (DTNBP1) associated with multiple psychiatric disorders including schizophrenia.Behav Brain Funct. 2010 Jul 9;6:41. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-6-41. Behav Brain Funct. 2010. PMID: 20615259 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep/Wake Disruption in a Mouse Model of BLOC-1 Deficiency.Front Neurosci. 2018 Nov 15;12:759. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00759. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30498428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Straub R.E., Jiang Y., MacLean C.J., Ma Y., Webb B.T., Myakishev M.V., Harris-Kerr C., Wormley B., Sadek H., Kadambi B., et al. Genetic variation in the 6p22.3 gene DTNBP1, the human ortholog of the mouse dysbindin gene, is associated with schizophrenia. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002;7:337–348. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Williams N.M., O'Donovan M.C., Owen M.J. Is the dysbindin gene (DTNBP1) a susceptibility gene for schizophrenia? Schizophr. Bull. 2005;31:800–805. - PubMed
-
- Riley B., Kendler K.S. Molecular genetic studies of schizophrenia. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2006;14:669–680. - PubMed
-
- Talbot K., Ong W.Y., Blake D.J., Tang J., Louneva N., Carlson G.C., Arnold S.E. Dysbindin-1 and its protein family with special attention to the potential role of dysbindin-1 in neuronal functions and the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. In: Javitt D., Kantorowitz J., editors. Handbook of Neurochemistry and Molecular Neurobiology. 3rd edn. Vol. 27. New York: Springer Scientific; 2009. (in press)
-
- Allen N.C., Bagade S., McQueen M.B., Ioannidis J.P.A., Kavvoura F.K., Khoury M.J., Tanzi R.E., Bertram L. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat. Genet. 2008;40:827–834. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

