Interleukin-2 cycling causes transient increases in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and D-dimer that are not associated with plasma HIV-RNA levels
- PMID: 19617815
- PMCID: PMC2760947
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832d72c6
Interleukin-2 cycling causes transient increases in high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and D-dimer that are not associated with plasma HIV-RNA levels
Abstract
Objective: To determine the effects of interleukin (IL)-2 treatment on inflammatory and thrombotic biomarkers in chronically HIV-infected adults receiving antiretroviral therapy.
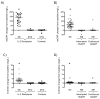
Methods: Cryopreserved plasma was evaluated retrospectively for C-reactive protein (CRP) and D-dimer at baseline, end of an IL-2 cycle, and long-term follow up from two randomized, controlled trials: 57 IL-2-naive adults receiving either three to six cycles of IL-2 as well as antiretroviral therapy (nucleoside analogues) or antiretroviral therapy alone for 12 months, and 40 IL-2-experienced adults on highly active antiretroviral therapy who either interrupted or continued therapy for 6 months after a baseline IL-2 cycle. High-sensitivity CRP (hsCRP) was measured by immunonephelometry (detection limit 0.175 mg/l) and D-dimer by latex agglutination (detection limit 0.20 mg/l). Median within-group differences and pre and post-IL-2 changes between groups were assessed via nonparametric Wilcoxon signed-rank and Mann-Whitney U-tests. Spearman's rank test was used to assess correlations between changes in hsCRP, D-dimer, and HIV-RNA viral load.
Results: Significant increases in hsCRP (study 1: 138.6 mg/l; study 2: 58.9 mg/l) and D-dimer (study 1: 3.1 mg/l; study 2: 0.4 mg/l, all P < 0.0001) occurred by the end of the initial IL-2 cycle, returning to baseline by the end of study. No correlations were seen between changes in hsCRP or D-dimer and HIV-RNA, CD4 T-cell count, or proliferation (Ki67 expression). No thrombotic or cardiovascular serious adverse events occurred during these study periods.
Conclusion: IL-2 dosing caused transient increases in plasma hsCRP and D-dimer levels, regardless of HIV-RNA viral load, suggesting the possibility of increased risk for thrombotic events.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Changes in the levels of some acute-phase proteins in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected patients, following interleukin-2 treatment.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;161(1):134-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04145.x. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20408859 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory biomarkers and abacavir use in the Women's Interagency HIV Study and the Multicenter AIDS Cohort Study.AIDS. 2010 Jul 17;24(11):1657-65. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e3283389dfa. AIDS. 2010. PMID: 20588104 Free PMC article.
-
Higher levels of CRP, D-dimer, IL-6, and hyaluronic acid before initiation of antiretroviral therapy (ART) are associated with increased risk of AIDS or death.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jun 1;203(11):1637-46. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir134. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21592994 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Role of interleukin-2 in patients with HIV infection.Drugs. 2010 Jun 18;70(9):1115-30. doi: 10.2165/10898620-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20518579 Review.
-
The Effect of Rosuvastatin on Plasma/Serum Levels of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, and D-Dimer in People Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021 Nov;37(11):821-833. doi: 10.1089/AID.2020.0273. Epub 2021 Jun 14. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2021. PMID: 33913752
Cited by
-
Soluble mediators of inflammation in HIV and their implications for therapeutics and vaccine development.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012 Aug-Oct;23(4-5):193-206. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2012.05.006. Epub 2012 Jun 27. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2012. PMID: 22743035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Changes in the levels of some acute-phase proteins in human immunodeficiency virus-1 infected patients, following interleukin-2 treatment.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Jul 1;161(1):134-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04145.x. Epub 2010 Apr 9. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20408859 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors of bacterial pneumonia in Evaluation of Subcutaneous Interleukin-2 in a Randomized International Trial (ESPRIT).HIV Med. 2011 Apr;12(4):219-27. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2010.00875.x. Epub 2010 Aug 31. HIV Med. 2011. PMID: 20812949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Paradoxical tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) in HIV patients with culture confirmed pulmonary tuberculosis in India and the potential role of IL-6 in prediction.PLoS One. 2013 May 17;8(5):e63541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063541. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23691062 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Quantifying and predicting the effect of exogenous interleukin-7 on CD4+ T cells in HIV-1 infection.PLoS Comput Biol. 2014 May 22;10(5):e1003630. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003630. eCollection 2014 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2014. PMID: 24853554 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arduino RC, Nannini EC, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Schrader S, Losso M, Ruxrungtham K, et al. CD4 cell response to 3 doses of subcutaneous interleukin 2: meta-analysis of 3 Vanguard studies. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:115–122. - PubMed
-
- Farel CE, Chaitt DG, Hahn BK, Tavel JA, Kovacs JA, Polis MA, et al. Induction and maintenance therapy with intermittent interleukin-2 in HIV-1 infection. Blood. 2004;103:3282–3286. - PubMed
-
- Emery S, Abrams DI, Cooper DA, Darbyshire JH, Lane HC, Lundgren JD, Neaton JD. The evaluation of subcutaneous proleukin (interleukin-2) in a randomized international trial: rationale, design, and methods of ESPRIT. Control Clin Trials. 2002;23:198–220. - PubMed
-
- Pett SL, Wand H, Law MG, Arduino R, Lopez JC, Knysz B, et al. Evaluation of Subcutaneous Proleukin (interleukin-2) in a Randomized International Trial (ESPRIT): geographical and gender differences in the baseline characteristics of participants. HIV Clin Trials. 2006;7:70–85. - PubMed
-
- Levy Y. Effect of interleukin-2 (IL-2) on clinical outcomes in patients with CD4+ cell count 50–299/mm3: Primary results of the SILCAAT Study. 16th Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections; Montreal, Canada. 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

