Assessment of the low-cost Cavidi ExaVir Load assay for monitoring HIV viral load in pediatric and adult patients
- PMID: 19617845
- PMCID: PMC2784031
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181b05f62
Assessment of the low-cost Cavidi ExaVir Load assay for monitoring HIV viral load in pediatric and adult patients
Abstract
Background: Viral load (VL) is a critical marker for monitoring HIV disease progression and response to antiretroviral therapy. In resource-constrained settings, there is a need for a simple and inexpensive assay to monitor infected adults and children.
Methods: We compared versions 2 and 3 of the ExaVir Load assay, Cavidi AB (HIV RT) with the Roche, COBAS Amplicor HIV-1 Monitor assay (HIV RNA) for quantifying HIV VL.
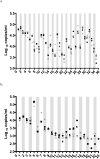
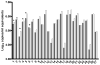
Results: The HIV RT version 2 assay showed good sensitivity with detection in 94% of samples with HIV RNA >1000 copies per milliliter. Adult samples were tested using HIV RT version 2 (n = 35) and version 3 (n = 23) assays with plasma volumes of 1 mL (recommended), 0.5 mL and 0.25 mL in comparison with HIV RNA. The HIV RT and HIV RNA assay results were comparable when tested using different volumes. Comparison of results from pediatric samples (n = 27), tested using 1 mL and a smaller volume by HIV RT version 2 were not significantly different.
Conclusions: The HIV RT assay was comparable to the HIV RNA assay with sensitivity approaching that of HIV RNA. Smaller volumes than the recommended 1 mL can be used, improving utility of this assay for pediatric monitoring.
Figures
References
-
- Crowe S, Turnbull S, Oelrichs R, et al. Monitoring of human immunodeficiency virus infection in resource-constrained countries. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(Suppl 1):S25–35. - PubMed
-
- Rouet F, Rouzioux C. The measurement of HIV-1 viral load in resource-limited settings: how and where? Clin Lab. 2007;53(3–4):135–148. - PubMed
-
- Malmsten A, Shao XW, Sjodahl S, et al. Improved HIV-1 viral load determination based on reverse transcriptase activity recovered from human plasma. J Med Virol. 2005;76(3):291–296. - PubMed
-
- Kamat A, Ravi V, Desai A, et al. Quantitation of HIV-1 RNA levels in plasma and CSF of asymptomatic HIV-1 infected patients from South India using a TaqMan real time PCR assay. J Clin Virol. 2007;39(1):9–15. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

