Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in adults: treatment results after long-term follow-up with special reference to adjuvant interferon-beta in undifferentiated carcinomas
- PMID: 19618214
- PMCID: PMC2779341
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-009-0640-2
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma in adults: treatment results after long-term follow-up with special reference to adjuvant interferon-beta in undifferentiated carcinomas
Abstract
Purpose: Nasopharyngeal carcinomas (NPC) are radiosensitive, and radiotherapy is the standard curative treatment. Furthermore, it has been shown that combined radiochemotherapy improves prognosis in locally advanced stages. Further encouraging results have been obtained with adjuvant interferon-beta after primary radio(chemo)therapy in childhood undifferentiated NPC. Aim of the present study was to evaluate the treatment results after long-term follow-up after radio(chemo)therapy for adult NPC with special reference to patients with undifferentiated carcinomas treated with adjuvant interferon-beta.
Patients and methods: From 02/1992 to 07/2008, 26 adult patients with NPC without distant metastases were treated (17 squamous cell carcinomas, 9 undifferentiated carcinomas). The treatment concepts changed over the years: 13 patients were treated with radiotherapy alone, 13 patients received combined radiochemotherapy. Additionally, six patients with undifferentiated carcinomas were treated with adjuvant interferon-beta after radiochemotherapy for 6 months.
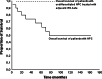
Results: After a median follow-up of 96 months, 17 patients remain alive. Collectively, our 5-year overall-survival and loco-regional control rates were 74% (radiochemotherapy 81%, radiotherapy alone 68.5%) and 87% (radiochemotherapy 100%, radiotherapy alone 72.7%), respectively. All treatment regimens used were feasible; especially, adjuvant interferon-beta was applied as provided without high grade toxicity. All patients with undifferentiated carcinomas treated with adjuvant interferon-beta stayed alive until the end of the follow-up.
Conclusion: In summary, our data affirm that NPC in adults are curable by primary radio(chemo)therapy. Furthermore, our data indicate that adjuvant interferon-beta application in undifferentiated NPC in adults is feasible and shows promising results. Further prospective clinical trials are needed to finally establish adjuvant interferon beta in curative treatment of adult NPC.
Figures

References
-
- Baujat B, Audry H, Bourhis J, Chan AT, Onat H, Chua DT, Kwong DL, Al-Sarraf M, Chi KH, Hareyama M et al (2006) Chemotherapy in locally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an individual patient data meta-analysis of eight randomized trials and 1753 patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:47–56 - PubMed
-
- Castellsague X (2008) Natural history and epidemiology of HPV infection and cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol 110:S4–S7 - PubMed
-
- Chan AT, Leung SF, Ngan RK, Teo PM, Lau WH, Kwan WH, Hui EP, Yiu HY, Yeo W, Cheung FY et al (2005) Overall survival after concurrent cisplatin-radiotherapy compared with radiotherapy alone in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 97:536–539 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

