Discovery of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors using metabolomics biased fragment crystallography
- PMID: 19618939
- PMCID: PMC2722745
- DOI: 10.1021/jm900259h
Discovery of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors using metabolomics biased fragment crystallography
Erratum in
- J Med Chem. 2010 Mar 11;53(5):2330-1
Abstract
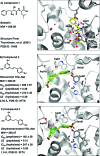
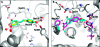
We describe a novel fragment library termed fragments of life (FOL) for structure-based drug discovery. The FOL library includes natural small molecules of life, derivatives thereof, and biaryl protein architecture mimetics. The choice of fragments facilitates the interrogation of protein active sites, allosteric binding sites, and protein-protein interaction surfaces for fragment binding. We screened the FOL library against leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H) by X-ray crystallography. A diverse set of fragments including derivatives of resveratrol, nicotinamide, and indole were identified as efficient ligands for LTA4H. These fragments were elaborated in a small number of synthetic cycles into potent inhibitors of LTA4H representing multiple novel chemotypes for modulating leukotriene biosynthesis. Analysis of the fragment-bound structures also showed that the fragments comprehensively recapitulated key chemical features and binding modes of several reported LTA4H inhibitors.
Figures










Similar articles
-
Thermodynamic properties of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2016 Nov 1;24(21):5243-5248. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2016.08.047. Epub 2016 Aug 26. Bioorg Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 27651294
-
Feasibility and physiological relevance of designing highly potent aminopeptidase-sparing leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 19;7(1):13591. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-13490-1. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29051536 Free PMC article.
-
Dual anti-inflammatory and selective inhibition mechanism of leukotriene A4 hydrolase/aminopeptidase: insights from comparative molecular dynamics and binding free energy analyses.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016 Nov;34(11):2418-33. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2015.1117991. Epub 2016 Jan 11. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2016. PMID: 26555301
-
Overview of recent drug discovery approaches for new generation leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitors.Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013 Jan;8(1):49-63. doi: 10.1517/17460441.2013.735228. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Expert Opin Drug Discov. 2013. PMID: 23095029 Review.
-
Leukotriene A4 hydrolase as a target for cancer prevention and therapy.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004 May;4(3):267-83. doi: 10.2174/1568009043333041. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004. PMID: 15134534 Review.
Cited by
-
The development of novel LTA4H modulators to selectively target LTB4 generation.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 17;7:44449. doi: 10.1038/srep44449. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28303931 Free PMC article.
-
Di- and tripeptide transport in vertebrates: the contribution of teleost fish models.J Comp Physiol B. 2017 Apr;187(3):395-462. doi: 10.1007/s00360-016-1044-7. Epub 2016 Nov 1. J Comp Physiol B. 2017. PMID: 27803975 Review.
-
A glutathione peroxidase, intracellular peptidases and the TOR complexes regulate peptide transporter PEPT-1 in C. elegans.PLoS One. 2011;6(9):e25624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025624. Epub 2011 Sep 28. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21980510 Free PMC article.
-
Structural origins for the loss of catalytic activities of bifunctional human LTA4H revealed through molecular dynamics simulations.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041063. Epub 2012 Jul 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22848428 Free PMC article.
-
An ensemble of structures of Burkholderia pseudomallei 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate-dependent phosphoglycerate mutase.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011 Sep 1;67(Pt 9):1044-50. doi: 10.1107/S1744309111030405. Epub 2011 Aug 13. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2011. PMID: 21904048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tan X.; Calderon-Villalobos L. I.; Sharon M.; Zheng C.; Robinson C. V.; Estelle M.; Zheng N. Mechanism of auxin perception by the TIR1 ubiquitin ligase. Nature 2007, 446, 640–645. - PubMed
-
- Shimada A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka M.; Nakatsu T.; Nakajima M.; Naoe Y.; Ohmiya H.; Kato H.; Matsuoka M. Structural basis for gibberellin recognition by its receptor GID1. Nature 2008, 456, 520–523. - PubMed
-
- Wishart D. S.; Knox C.; Guo A. C.; Eisner R.; Young N.; Gautam B.; Hau D. D.; Psychogios N.; Dong E.; Bouatra S.; Mandal R.; Sinelnikov I.; Xia J.; Jia L.; Cruz J. A.; Lim E.; Sobsey C. A.; Shrivastava S.; Huang P.; Liu P.; Fang L.; Peng J.; Fradette R.; Cheng D.; Tzur D.; Clements M.; Lewis A.; De Souza A.; Zuniga A.; Dawe M.; Xiong Y.; Clive D.; Greiner R.; Nazyrova A.; Shaykhutdinov R.; Li L.; Vogel H. J.; Forsythe I. HMDB: a knowledgebase for the human metabolome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 37 (Database Issue), D603–D610. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

