Human S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase: common gene sequence variation and functional genomic characterization
- PMID: 19619139
- PMCID: PMC2838417
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06276.x
Human S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase: common gene sequence variation and functional genomic characterization
Abstract
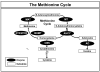
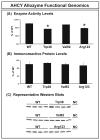
S-Adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (AHCY) is the only mammalian enzyme known to catalyze the hydrolysis of S-adenosylhomocysteine. We have used a genotype-to-phenotype strategy to study this important enzyme by resequencing AHCY in 240 DNA samples from four ethnic groups. Thirty-nine polymorphisms were identified - 28 of which were novel. Functional genomic studies for wild type AHCY and the three variant allozymes identified showed that two variant allozymes had slight, but significant decreases in enzyme activity, but with no significant differences in levels of immunoreactive protein. Luciferase reporter gene assays for common 5'-flanking region haplotypes revealed that one haplotype with a frequency of approximately 2% in Caucasian-American subjects displayed a decreased ability to drive transcription. The variant nucleotide at 5'-flanking region single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) (-34) in that haplotype altered the DNA-protein binding pattern during electrophoresis mobility shift assay. Finally, an AHCY genotype-phenotype association study for expression in lymphoblastoid cells identified four SNPs that were associated with decreased expression. For the IVS6 (intervening sequence 6, i.e., intron 6) G56 > C SNP among those four, electrophoresis mobility shift assay showed that a C > G nucleotide change resulted in an additional shifted band. These results represent a step toward understanding the functional consequences of common genetic variation in AHCY for the regulation of neurotransmitter, drug and macromolecule methylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Glutathione s-transferase p1: gene sequence variation and functional genomic studies.Cancer Res. 2008 Jun 15;68(12):4791-801. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6724. Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18559526 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase (AHCY) affect its nucleocytoplasmic distribution and capability to interact with S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase-like 1 protein.Eur J Cell Biol. 2017 Sep;96(6):579-590. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2017.05.002. Epub 2017 May 13. Eur J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28647132
-
Human methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase pharmacogenomics: gene resequencing and functional genomics.Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2006 Apr;16(4):265-77. doi: 10.1097/01.fpc.0000194423.20393.08. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 2006. PMID: 16538173
-
Functional and Pathological Roles of AHCY.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar 31;9:654344. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.654344. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33869213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The IRBIT domain adds new functions to the AHCY family.Bioessays. 2008 Jul;30(7):642-52. doi: 10.1002/bies.20772. Bioessays. 2008. PMID: 18536033 Review.
Cited by
-
Downregulation of genes involved in metabolism and oxidative stress in the peripheral leukocytes of Huntington's disease patients.PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e46492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046492. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23029535 Free PMC article.
-
Human liver methionine cycle: MAT1A and GNMT gene resequencing, functional genomics, and hepatic genotype-phenotype correlation.Drug Metab Dispos. 2012 Oct;40(10):1984-92. doi: 10.1124/dmd.112.046953. Epub 2012 Jul 17. Drug Metab Dispos. 2012. PMID: 22807109 Free PMC article.
-
A common functional promoter variant links CNR1 gene expression to HDL cholesterol level.Nat Commun. 2013;4:1973. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2973. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 23748922 Free PMC article.
-
Knock-down of AHCY and depletion of adenosine induces DNA damage and cell cycle arrest.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 18;8(1):14012. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-32356-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30228286 Free PMC article.
-
Betaine-homocysteine methyltransferase: human liver genotype-phenotype correlation.Mol Genet Metab. 2011 Feb;102(2):126-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2010.10.010. Epub 2010 Oct 21. Mol Genet Metab. 2011. PMID: 21093336 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ando T, Kojima K, Chahota P, Kozaki A, Milind ND, Kitade Y. Synthesis of 4′-modified noraristeromycins to clarify the effect of the 4′-hydroxyl groups for inhibitory activity against S-adenosyl-L-homocysteine hydrolase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2008;18:2615–2618. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J. The enzymatic N-methylation of serotonin and other amines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1962a;138:28–33. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J. Purification and properties of phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase. J Biol Chem. 1962b;237:1657–1660. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J, Cohn CK. Methyltransferase enzymes in red blood cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971;176:650–654. - PubMed
-
- Axelrod J, Tomchick R. Enzymatic O-methylation of epinephrine and other catechols. J Biol Chem. 1958;233:702–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

