Analysis of intraindividual and intraspecific variation in semicircular canal dimensions using high-resolution x-ray computed tomography
- PMID: 19619167
- PMCID: PMC2766062
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01124.x
Analysis of intraindividual and intraspecific variation in semicircular canal dimensions using high-resolution x-ray computed tomography
Abstract
The semicircular canal system tracks head rotation and provides sensory input for the reflexive stabilization of gaze and posture. The purpose of this study was to investigate the intraspecific and intraindividual variation in the size of the three semicircular canals. The right and left temporal bones were extracted from 31 individuals of the short-tailed shrew (Blarina brevicauda) and scanned on a high-resolution x-ray computed tomography system. The radius of curvature was calculated for each of the three semicircular canals for each side. Paired t-tests and independent sample t-tests indicated no significant differences in canal size between the right and left canals of the same individuals or between those of males and females of the same species. Pearson product moment correlation analyses demonstrated that there was no significant correlation between canal size and body mass in this sample.
Figures
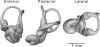


Similar articles
-
Semicircular canals and agility: the influence of size and shape measures.J Anat. 2010 Jan;216(1):37-47. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7580.2009.01172.x. Epub 2009 Nov 25. J Anat. 2010. PMID: 20002227 Free PMC article.
-
Eye size and visual acuity influence vestibular anatomy in mammals.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014 Apr;297(4):781-90. doi: 10.1002/ar.22892. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014. PMID: 24591307
-
Brief communication: Investigation of the semicircular canal variation in the Krapina Neandertals.Am J Phys Anthropol. 2014 Jun;154(2):302-6. doi: 10.1002/ajpa.22506. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Am J Phys Anthropol. 2014. PMID: 24610299
-
CT and MRI of the semicircular canals in the normal and diseased temporal bone.Eur Radiol. 2001;11(7):1210-9. doi: 10.1007/s003300000703. Eur Radiol. 2001. PMID: 11471615 Review.
-
Semicircular Canal Size and Shape Influence on Disorientation.Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2018 Aug 1;89(8):744-748. doi: 10.3357/AMHP.5104.2018. Aerosp Med Hum Perform. 2018. PMID: 30020060 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the ontogenetic development of the inner ear in Aardvarks.J Anat. 2021 May;238(5):1128-1142. doi: 10.1111/joa.13361. Epub 2020 Dec 21. J Anat. 2021. PMID: 33345316 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of bat vestibular systems in the face of potential antagonistic selection pressures for flight and echolocation.PLoS One. 2013 Apr 24;8(4):e61998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061998. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23637943 Free PMC article.
-
Intraspecific variation and symmetry of the inner-ear labyrinth in a population of wild turkeys: implications for paleontological reconstructions.PeerJ. 2019 Jul 23;7:e7355. doi: 10.7717/peerj.7355. eCollection 2019. PeerJ. 2019. PMID: 31372322 Free PMC article.
-
Somatosensory organ topography across the star of the star-nosed mole (Condylura cristata).J Comp Neurol. 2016 Apr 1;524(5):917-29. doi: 10.1002/cne.23943. Epub 2015 Dec 29. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26659700 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of Normal Semi-circular Canal Dimensions on Computed Tomography.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023 Apr;75(Suppl 1):176-180. doi: 10.1007/s12070-022-03331-7. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2023. PMID: 37206736 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anson BJ, Bast TH. The development of the otic capsule in the region of surgical fenestration. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1949;58:739–750. - PubMed
-
- Blanks RH, Curthoys IS, Bennett ML, Markham CH. Planar relationships of the semicircular canals in rhesus and squirrel monkeys. Brain Res. 1985;340:315–324. - PubMed
-
- Braun JK, Kennedy ML. Systematics of the genus Blarina in Tennessee and adjacent areas. J Mammal. 1983;64:414–425.
-
- Choate JR. Variation within and among populations of short-tailed shrew in Connecticut. J Mammal. 1972;53:116–128.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

