A comparison of RNA amplification techniques at sub-nanogram input concentration
- PMID: 19619282
- PMCID: PMC2724417
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-326
A comparison of RNA amplification techniques at sub-nanogram input concentration
Abstract
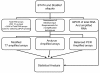
Background: Gene expression profiling of small numbers of cells requires high-fidelity amplification of sub-nanogram amounts of RNA. Several methods for RNA amplification are available; however, there has been little consideration of the accuracy of these methods when working with very low-input quantities of RNA as is often required with rare clinical samples. Starting with 250 picograms-3.3 nanograms of total RNA, we compared two linear amplification methods 1) modified T7 and 2) Arcturus RiboAmp HS and a logarithmic amplification, 3) Balanced PCR. Microarray data from each amplification method were validated against quantitative real-time PCR (QPCR) for 37 genes.
Results: For high intensity spots, mean Pearson correlations were quite acceptable for both total RNA and low-input quantities amplified with each of the 3 methods. Microarray filtering and data processing has an important effect on the correlation coefficient results generated by each method. Arrays derived from total RNA had higher Pearson's correlations than did arrays derived from amplified RNA when considering the entire unprocessed dataset, however, when considering a gene set of high signal intensity, the amplified arrays had superior correlation coefficients than did the total RNA arrays.
Conclusion: Gene expression arrays can be obtained with sub-nanogram input of total RNA. High intensity spots showed better correlation on array-array analysis than did unfiltered data, however, QPCR validated the accuracy of gene expression array profiling from low-input quantities of RNA with all 3 amplification techniques. RNA amplification and expression analysis at the sub-nanogram input level is both feasible and accurate if data processing is used to focus attention to high intensity genes for microarrays or if QPCR is used as a gold standard for validation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Validation and application of a high fidelity mRNA linear amplification procedure for profiling gene expression.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005 May 15;105(3-4):331-42. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2005.02.018. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2005. PMID: 15808310
-
Fidelity and enhanced sensitivity of differential transcription profiles following linear amplification of nanogram amounts of endothelial mRNA.Physiol Genomics. 2003 Apr 16;13(2):147-56. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00173.2002. Physiol Genomics. 2003. PMID: 12700361
-
Microarray-based comparison of three amplification methods for nanogram amounts of total RNA.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005 May;288(5):C1179-89. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00258.2004. Epub 2004 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005. PMID: 15613496 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for microarray analysis of limiting amounts of RNA.Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003 Apr;2(1):31-6. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/2.1.31. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic. 2003. PMID: 15239941 Review.
-
Disease profiling arrays: reverse format cDNA arrays complimentary to microarrays.Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004;86:191-213. doi: 10.1007/b12443. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15088766 Review.
Cited by
-
Insight into insulin secretion from transcriptome and genetic analysis of insulin-producing cells of Drosophila.Genetics. 2014 May;197(1):175-92. doi: 10.1534/genetics.113.160663. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Genetics. 2014. PMID: 24558258 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Isolation and Gene Analysis: Pitfalls and Possibilities.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 10;16(11):26832-49. doi: 10.3390/ijms161125996. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26569222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The potential for liquid biopsies in the precision medical treatment of breast cancer.Cancer Biol Med. 2016 Mar;13(1):19-40. doi: 10.28092/j.issn.2095-3941.2016.0007. Cancer Biol Med. 2016. PMID: 27144060 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting spatio-temporal protein networks driving human heart development and related disorders.Mol Syst Biol. 2010 Jun 22;6:381. doi: 10.1038/msb.2010.36. Mol Syst Biol. 2010. PMID: 20571530 Free PMC article.
-
Global array-based transcriptomics from minimal input RNA utilising an optimal RNA isolation process combined with SPIA cDNA probes.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 22;6(3):e17625. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017625. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21445340 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

