Spine imaging after lumbar disc replacement: pitfalls and current recommendations
- PMID: 19619332
- PMCID: PMC2716308
- DOI: 10.1186/1754-9493-3-15
Spine imaging after lumbar disc replacement: pitfalls and current recommendations
Abstract
Background: Most lumbar artificial discs are still composed of stainless steel alloys, which prevents adequate postoperative diagnostic imaging of the operated region when using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Thus patients with postoperative radicular symptoms or claudication after stainless steel implants often require alternative diagnostic procedures.
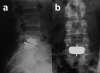
Methods: Possible complications of lumbar total disc replacement (TDR) are reviewed from the available literature and imaging recommendations given with regard to implant type. Two illustrative cases are presented in figures.
Results: Access-related complications, infections, implant wear, loosening or fracture, polyethylene inlay dislodgement, facet joint hypertrophy, central stenosis, and ankylosis of the operated segment can be visualised both in titanium and stainless steel implants, but require different imaging modalities due to magnetic artifacts in MRI.
Conclusion: Alternative radiographic procedures should be considered when evaluating patients following TDR. Postoperative complications following lumbar TDR including spinal stenosis causing radiculopathy and implant loosening can be visualised by myelography and radionucleotide techniques as an adjunct to plain film radiographs. Even in the presence of massive stainless steel TDR implants lumbar radicular stenosis and implant loosening can be visualised if myelography and radionuclide techniques are applied.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lumbar total disc replacement impingement sensitivity to disc height distraction, spinal sagittal orientation, implant position, and implant lordosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012 May 1;37(10):E590-8. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e318241e415. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012. PMID: 22146286
-
Total lumbar disc replacement: different results for different levels.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007 Apr 1;32(7):782-90. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000259071.64027.04. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2007. PMID: 17414914 Clinical Trial.
-
Biomaterial optimization in total disc arthroplasty.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003 Oct 15;28(20):S139-52. doi: 10.1097/01.BRS.0000092214.87225.80. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003. PMID: 14560185
-
A new classification system for degenerative disc disease of the lumbar spine based on magnetic resonance imaging, provocative discography, plain radiographs and anatomic considerations.Spine J. 2004 Nov-Dec;4(6 Suppl):167S-172S. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2004.07.001. Spine J. 2004. PMID: 15541662 Review.
-
Evaluation of Aesculap Implant Systems activl Artificial Disc for the treatment of degenerative disc disease.Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016 Dec;13(12):1069-1072. doi: 10.1080/17434440.2016.1256771. Epub 2016 Nov 22. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2016. PMID: 27807981 Review.
Cited by
-
Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation after implantation of a titanium cervical disc prosthesis: a comparison of 1.5 and 3 Tesla magnet strength.Eur Spine J. 2013 Oct;22(10):2296-302. doi: 10.1007/s00586-013-2994-z. Epub 2013 Sep 6. Eur Spine J. 2013. PMID: 24061966 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Biomechanical effects of semi-constrained integrated artificial discs on zygapophysial joints of implanted lumbar segments.Exp Ther Med. 2013 Dec;6(6):1423-1430. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1313. Epub 2013 Sep 26. Exp Ther Med. 2013. PMID: 24255672 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral femoral neck fractures after an epileptic attack: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;6C:107-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 13. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015. PMID: 25528038 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsuura H, Inoue T, Konno H, Sasaki M, Ogasawara K, Ogawa A. Quantification of susceptibility artifacts produced on high-field magnetic resonance images by various biomaterials used for neurosurgical implants. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 2002;97:1472–5. doi: 10.3171/jns.2002.97.6.1472. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suh JS, Jeong EK, Shin KH, Cho JH, Na JB, Kim DH, Han CD. Minimizing artifacts caused by metallic implants at MR imaging: experimental and clinical studies. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;171:1207–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

