Multisensory connections of monkey auditory cerebral cortex
- PMID: 19619628
- PMCID: PMC2788085
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heares.2009.06.019
Multisensory connections of monkey auditory cerebral cortex
Abstract
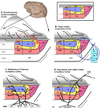
Functional studies have demonstrated multisensory responses in auditory cortex, even in the primary and early auditory association areas. The features of somatosensory and visual responses in auditory cortex suggest that they are involved in multiple processes including spatial, temporal and object-related perception. Tract tracing studies in monkeys have demonstrated several potential sources of somatosensory and visual inputs to auditory cortex. These include potential somatosensory inputs from the retroinsular (RI) and granular insula (Ig) cortical areas, and from the thalamic posterior (PO) nucleus. Potential sources of visual responses include peripheral field representations of areas V2 and prostriata, as well as the superior temporal polysensory area (STP) in the superior temporal sulcus, and the magnocellular medial geniculate thalamic nucleus (MGm). Besides these sources, there are several other thalamic, limbic and cortical association structures that have multisensory responses and may contribute cross-modal inputs to auditory cortex. These connections demonstrated by tract tracing provide a list of potential inputs, but in most cases their significance has not been confirmed by functional experiments. It is possible that the somatosensory and visual modulation of auditory cortex are each mediated by multiple extrinsic sources.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multisensory convergence in auditory cortex, I. Cortical connections of the caudal superior temporal plane in macaque monkeys.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Jun 20;502(6):894-923. doi: 10.1002/cne.21325. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17447261
-
Multisensory convergence in auditory cortex, II. Thalamocortical connections of the caudal superior temporal plane.J Comp Neurol. 2007 Jun 20;502(6):924-52. doi: 10.1002/cne.21326. J Comp Neurol. 2007. PMID: 17444488
-
Sources of somatosensory input to the caudal belt areas of auditory cortex.Perception. 2007;36(10):1419-30. doi: 10.1068/p5841. Perception. 2007. PMID: 18265825
-
Anatomy of the auditory cortex.Rev Neurol (Paris). 1995 Aug-Sep;151(8-9):486-94. Rev Neurol (Paris). 1995. PMID: 8578069 Review.
-
Do the Different Sensory Areas Within the Cat Anterior Ectosylvian Sulcal Cortex Collectively Represent a Network Multisensory Hub?Multisens Res. 2018 Jan;31(8):793-823. doi: 10.1163/22134808-20181316. Epub 2018 Jun 26. Multisens Res. 2018. PMID: 31157160 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sound-driven enhancement of vision: disentangling detection-level from decision-level contributions.J Neurophysiol. 2013 Feb;109(4):1065-77. doi: 10.1152/jn.00226.2012. Epub 2012 Dec 5. J Neurophysiol. 2013. PMID: 23221404 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Influences on Auditory Behavioral, Neural, and Perceptual Processes: A Review.J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2021 Jul;22(4):365-386. doi: 10.1007/s10162-021-00789-0. Epub 2021 May 20. J Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 34014416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A simpler primate brain: the visual system of the marmoset monkey.Front Neural Circuits. 2014 Aug 8;8:96. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2014.00096. eCollection 2014. Front Neural Circuits. 2014. PMID: 25152716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalamic influences on multisensory integration.Commun Integr Biol. 2011 Jul;4(4):378-81. doi: 10.4161/cib.15222. Epub 2011 Jul 1. Commun Integr Biol. 2011. PMID: 21966551 Free PMC article.
-
Auditory adaptation improves tactile frequency perception.J Neurophysiol. 2017 Mar 1;117(3):1352-1362. doi: 10.1152/jn.00783.2016. Epub 2017 Jan 11. J Neurophysiol. 2017. PMID: 28077668 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen RA, Roth GL, Aitkin LM, Merzenich MM. The efferent projections of the central nucleus and the pericentral nucleus of the inferior colliculus in the cat. J Comp Neurol. 1980;194(3):649–662. - PubMed
-
- Antal A, Baudewig J, Paulus W, Dechent P. The posterior cingulate cortex and planum temporale/parietal operculum are activated by coherent visual motion. Vis Neurosci. 2008;25(1):17–26. - PubMed
-
- Apkarian AV, Hodge CJ. Primate spinothalamic pathways: III. Thalamic terminations of the dorsolateral and ventral spinothalamic pathways. J Comp Neurol. 1989;288(3):493–511. - PubMed
-
- Avanzini G, Broggi G, Franceschetti S, Spreafico R. Multisensory convergence and interaction in the pulvinar-lateralis posterior complex of the cat's thalamus. Neurosci Lett. 1980;19(1):27–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

