Depurinating naphthalene-DNA adducts in mouse skin related to cancer initiation
- PMID: 19619639
- PMCID: PMC4424927
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.07.020
Depurinating naphthalene-DNA adducts in mouse skin related to cancer initiation
Abstract
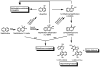
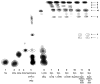
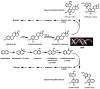
Naphthalene has been shown to be a weak carcinogen in rats. To investigate its mechanism of metabolic activation and cancer initiation, mice were topically treated with naphthalene or one of its metabolites, 1-naphthol, 1,2-dihydrodiolnaphthalene (1,2-DDN), 1,2-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,2-DHN), and 1,2-naphthoquinone (1,2-NQ). After 4 h, the mice were sacrificed, the treated skin was excised, and the depurinating and stable DNA adducts were analyzed. The depurinating adducts were identified and quantified by ultraperformance liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry, whereas the stable adducts were quantified by (32)P-postlabeling. For comparison, the stable adducts formed when a mixture of the four deoxyribonucleoside monophosphates was treated with 1,2-NQ or enzyme-activated naphthalene were also analyzed. The depurinating adducts 1,2-DHN-1-N3Ade and 1,2-DHN-1-N7Gua arise from reaction of 1,2-NQ with DNA. Similarly, the major stable adducts appear to derive from the 1,2-NQ. The depurinating DNA adducts are, in general, the most abundant. Therefore, naphthalene undergoes metabolic activation to the electrophilic ortho-quinone, 1,2-NQ, which reacts with DNA to form depurinating adducts. This is the same mechanism as other weak carcinogens, such as the natural and synthetic estrogens, and benzene.
Figures
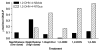
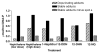
References
-
- Stanley JS. Environmental Protection Agency, office of toxic substances. Vol. 1. Washington, DC: 1986. Broad scan analysis of the FY82 national human adipose tissue survey specimens, executive summary (EPA-560/5-86-035)
-
- Pellizzari ED, Hartwell TD, Harris BSH, III, Waddell RD, Whitaker DA, Erickson MD. Purgeable organic compounds in mother’s milk. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1982;28:322–328. - PubMed
-
- Environmental Protection Agency. Clean air act amendments of 1990 conference report to accompany S. 1630. Office of Pollution Prevention and Toxics; Washington, DC: 1990. (Report No. 101–952)
-
- Buckpitt A, Boland B, Isbell M, Morin D, Shultz M, Baldwin R, Chan K, Karlsson A, Lin C, Taff A, West J, Fanucchi M, Van Winkle L, Plopper C. Naphthalene-induced respiratory tract toxicity: metabolic mechanisms of toxicity. Drug Metab Rev. 2002;34:791–820. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

