Burkitt's lymphoma: the Rosetta Stone deciphering Epstein-Barr virus biology
- PMID: 19619657
- PMCID: PMC3764430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2009.07.004
Burkitt's lymphoma: the Rosetta Stone deciphering Epstein-Barr virus biology
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus was originally identified in the tumour cells of a Burkitt's lymphoma, and was the first virus to be associated with the pathogenesis of a human cancer. Studies on the relationship of EBV with Burkitt's lymphoma have revealed important general principles that are relevant to other virus-associated cancers. In addition, the impact of such studies on the knowledge of EBV biology has been enormous. Here, we review some of the key historical observations arising from studies on Burkitt's lymphoma that have informed our understanding of EBV, and we summarise the current hypotheses regarding the role of EBV in the pathogenesis of Burkitt's lymphoma.
Figures
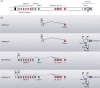
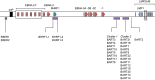
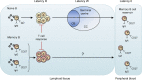
References
-
- Burkitt D. A sarcoma involving the jaws in African children. Br J Surg. 1958;46:218–223. - PubMed
-
- Burkitt D. A children's cancer dependent on climatic factors. Nature. 1962;194:232–234. - PubMed
-
- Epstein M.A., Achong B.G., Barr Y.M. Virus particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt's lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;i:702–703. - PubMed
-
- Rickinson A.B., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields virology. Walters Kluwer/Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Burkitt D.P. Etiology of Burkitt's lymphoma—an alternative hypothesis to a vectored virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969;42:19–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

