Emulation, imitation, over-imitation and the scope of culture for child and chimpanzee
- PMID: 19620112
- PMCID: PMC2865074
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0069
Emulation, imitation, over-imitation and the scope of culture for child and chimpanzee
Abstract
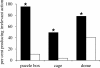
We describe our recent studies of imitation and cultural transmission in chimpanzees and children, which question late twentieth-century characterizations of children as imitators, but chimpanzees as emulators. As emulation entails learning only about the results of others' actions, it has been thought to curtail any capacity to sustain cultures. Recent chimpanzee diffusion experiments have by contrast documented a significant capacity for copying local behavioural traditions. Additionally, in recent 'ghost' experiments with no model visible, chimpanzees failed to replicate the object movements on which emulation is supposed to focus. We conclude that chimpanzees rely more on imitation and have greater cultural capacities than previously acknowledged. However, we also find that they selectively apply a range of social learning processes that include emulation. Recent studies demonstrating surprisingly unselective 'over-imitation' in children suggest that children's propensity to imitate has been underestimated too. We discuss the implications of these developments for the nature of social learning and culture in the two species. Finally, our new experiments directly address cumulative cultural learning. Initial results demonstrate a relative conservatism and conformity in chimpanzees' learning, contrasting with cumulative cultural learning in young children. This difference may contribute much to the contrast in these species' capacities for cultural evolution.
Figures


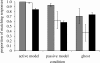

References
-
- Bonnie K. E., Horner V., Whiten A., de Waal F. B. M.2007Spread of arbitrary customs among chimpanzees: a controlled experiment. Proc. R. Soc. B. 274, 367–372 (doi:10.1098/rspb.2006.3733) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyd R., Richerson P. J.1996Why culture is common, but cultural evolution is rare. In Evolution of social behaviour patterns in primates and man (eds Runciman W. G., Maynard Smith J., Dunbar R. I. M.), pp. 77–93 Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press
-
- Brass M., Ruby P., Spengler S.2009Inhibition of imitative behaviour and social cognition. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 364, 2359–2367 (doi:10.1098/rstb.2009.0066) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buttelmann D., Carpenter M., Call J., Tomasello M.2007Enculturated chimpanzees imitate rationally. Dev. Sci. 10, 31–38 - PubMed
-
- Byrne R. W.2002Emulation in apes: verdict ‘not proven’. Dev. Sci. 5, 20–22 (doi:10.1111/1467-7687.00198) - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

