The role of the ADC value in the characterisation of renal carcinoma by diffusion-weighted MRI
- PMID: 19620174
- PMCID: PMC3473458
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr/74949757
The role of the ADC value in the characterisation of renal carcinoma by diffusion-weighted MRI
Abstract
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the role of diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in combination with T(1) and T(2) weighted MRI for the characterisation of renal carcinoma. The institutional review board approved the study protocols and waived informed consent from all of the patients. 47 patients (32 male and 15 female; age range, 21-85 years; median age, 65 years) who had suspected renal lesions on abdominal CT underwent MRI for further evaluation and characterisation of the lesions from April 2005 to August 2007 in our university hospital. A region of interest was drawn around the tumour area on apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps. Final diagnosis was confirmed by histological examination of surgical specimens from all patients. The ADC value was significantly higher in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) than in transitional cell carcinoma (2.71+/-2.35 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1) vs 1.61+/-0.80 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1); p = 0.022). While analysing the histological subtypes of RCC, a significant difference in ADC values between clear cell carcinoma and non-clear cell carcinoma was found (1.59+/-0.55 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1) vs 6.72+/-1.85 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1); p = 0.0004). Similarly, ADC values of RCC revealed a significant difference between positive and negative metastatic lesions (1.06+/-0.38 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1) vs 3.02+/-2.44 x 10(-3) mm(2) s(-1); p = 0.0004), whereas intensity on T(1) and T(2) weighted imaging did not reach statistical significance. In conclusion, DWI has clinical value in the characterisation of renal carcinomas and could be applied in clinical practice for their management.
Figures
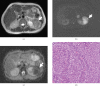


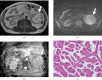


References
-
- Ng CS, Wood CG, Silverman PM, Tannir NM, Tamboli P, Sandler CM. Renal cell carcinoma: diagnosis, staging, and surveillance. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008;191:1220–32 - PubMed
-
- Dyer R, DiSantis DJ, McClennan BL. Simplified imaging approach for evaluation of the solid renal mass in adults. Radiology 2008;247:331–42 - PubMed
-
- Manenti G, Di Roma M, Mancino S, Bartolucci DA, Palmieri G, Mastrangeli R, et al. Malignant renal neoplasms: correlation between ADC values and cellularity in diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging at 3T. Radiol Med 2008;113:199–213 - PubMed
-
- Pedrosa I, Sun MR, Spencer M, Genega EM, Olumi AF, Dewolf WC, et al. MR imaging of renal masses: correlation with findings at surgery and pathologic analysis. RadioGraphics 2008;28:985–1003 - PubMed
-
- Takahara T, Imai Y, Yamashita T, Yasuda S, Nasu S, Van Cauteren M. Diffusion-weighted whole body imaging with background body signal suppression (DWIBS): technical improvement using free breathing, STIR and high resolution 3D display. Radiat Med 2004;22:275–82 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

