Chronic lung disease and developmental delay at 2 years of age in children born before 28 weeks' gestation
- PMID: 19620203
- PMCID: PMC2799188
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2008-2874
Chronic lung disease and developmental delay at 2 years of age in children born before 28 weeks' gestation
Abstract
Introduction: Extremely low gestational age newborns (ELGANs) are at increased risk of chronic lung disease (CLD) and of developmental delay. Some studies have suggested that CLD contributes to developmental delay.
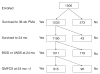
Patients and methods: We examined data collected prospectively on 915 infants born before the 28th week of gestation in 2002-2004 who were assessed at 24 months of age with the Bayley Scales of Infant Development-2nd Edition or the Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales. We excluded infants who were not able to walk independently (Gross Motor Function Classification System score < 1) and, therefore, more likely to have functionally important fine motor impairments. We defined CLD as receipt of oxygen at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age and classified infants as either not receiving mechanical ventilation (MV) (CLD without MV) or receiving MV (CLD with MV).
Results: Forty-nine percent of ELGANs had CLD; of these, 14% were receiving MV at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age. ELGANs without CLD had the lowest risk of a Mental Developmental Index (MDI) or a Psychomotor Developmental Index (PDI) of <55, followed by ELGANs with CLD not receiving MV, and ELGANs with CLD receiving MV (9%, 12%, and 18% for the MDI and 7%, 10%, and 20% for the PDI, respectively). In time-oriented multivariate models, the risk of an MDI of <55 was associated with the following variables: gestational age of <25 weeks; single mother; late bacteremia; pneumothorax; and necrotizing enterocolitis. The risk of a PDI of <55 was associated with variables such as single mother, a complete course of antenatal corticosteroids, early and persistent pulmonary dysfunction, pulmonary deterioration during the second postnatal week, pneumothorax, and pulmonary interstitial emphysema. CLD, without or with MV, was not associated with the risk of either a low MDI or a low PDI. However, CLD with MV approached, but did not achieve, nominal statistical significance (odds ratio: 1.9 [95% confidence interval: 0.97-3.9]) for the association with a PDI of <55.
Conclusions: Among children without severe gross motor delays, risk factors for CLD account for the association between CLD and developmental delay. Once those factors are considered in time-oriented risk models, CLD does not seem to increase the risk of either a low MDI or a low PDI. However, severe CLD might increase the risk of a low PDI.
References
-
- Vohr BR, Wright LL, Dusick AM, et al. Neurodevelopmental and functional outcomes of extremely low birth weight infants in the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Neonatal Research Network, 1993–1994. Pediatrics. 2000;105(6):1216–1226. - PubMed
-
- Fily A, Pierrat V, Delporte V, Breart G, Truffert P. Factors associated with neurodevelopmental outcome at 2 years after very preterm birth: the population-based Nord-Pas-de-Calais EPIPAGE cohort. Pediatrics. 2006;117(2):357–366. - PubMed
-
- Hughes CA, O'Gorman LA, Shyr Y, Schork MA, Bozynski ME, McCormick MC. Cognitive performance at school age of very low birth weight infants with bronchopulmonary dysplasia. J Dev Behav Pediatr. 1999;20(1):1–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases