Kinetic study of neuropeptide Y (NPY) proteolysis in blood and identification of NPY3-35: a new peptide generated by plasma kallikrein
- PMID: 19620246
- PMCID: PMC2757175
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.035253
Kinetic study of neuropeptide Y (NPY) proteolysis in blood and identification of NPY3-35: a new peptide generated by plasma kallikrein
Abstract
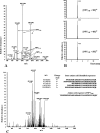
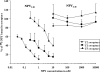
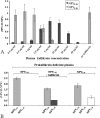
There is little information on how neuropeptide Y (NPY) proteolysis by peptidases occurs in serum, in part because reliable techniques are lacking to distinguish different NPY immunoreactive forms and also because the factors affecting the expression of these enzymes have been poorly studied. In the present study, LC-MS/MS was used to identify and quantify NPY fragments resulting from peptidolytic cleavage of NPY(1-36) upon incubation with human serum. Kinetic studies indicated that NPY(1-36) is rapidly cleaved in serum into 3 main fragments with the following order of efficacy: NPY(3-36) >> NPY(3-35) > NPY(2-36). Trace amounts of additional NPY forms were identified by accurate mass spectrometry. Specific inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase IV, kallikrein, and aminopeptidase P prevented the production of NPY(3-36), NPY(3-35), and NPY(2-36), respectively. Plasma kallikrein at physiological concentrations converted NPY(3-36) into NPY(3-35). Receptor binding assays revealed that NPY(3-35) is unable to bind to NPY Y1, Y2, and Y5 receptors; thus NPY(3-35) may represent the major metabolic clearance product of the Y2/Y5 agonist, NPY(3-36).
Figures


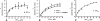

References
-
- Wahlestedt C., Edvinsson L., Ekblad E., Håkanson R. (1985) J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 234, 735–741 - PubMed
-
- Walker P., Grouzmann E., Burnier M., Waeber B. (1991) Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 12, 111–115 - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Samad D., Jacques D., Perreault C., Provost C. (2007) Peptides 28, 281–287 - PubMed
-
- Sahu A., Kalra S. P. (1993) Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 4, 217–224 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

