Novel molecular determinants in the pore region of sodium channels regulate local anesthetic binding
- PMID: 19620257
- PMCID: PMC2769053
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.109.055863
Novel molecular determinants in the pore region of sodium channels regulate local anesthetic binding
Abstract
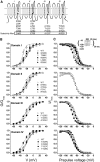
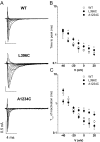
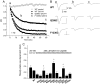
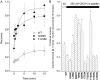
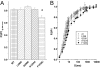
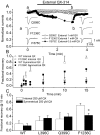
The pore of the Na+ channel is lined by asymmetric loops formed by the linkers between the fifth and sixth transmembrane segments (S5-S6). We investigated the role of the N-terminal portion (SS1) of the S5-S6 linkers in channel gating and local anesthetic (LA) block using site-directed cysteine mutagenesis of the rat skeletal muscle (Na(V)1.4) channel. The mutants examined have variable effects on voltage dependence and kinetics of fast inactivation. Of the cysteine mutants immediately N-terminal to the putative DEKA selectivity filter in four domains, only Q399C in domain I and F1236C in domain III exhibit reduced use-dependent block. These two mutations also markedly accelerated the recovery from use-dependent block. Moreover, F1236C and Q399C significantly decreased the affinity of QX-314 for binding to its channel receptor by 8.5- and 3.3-fold, respectively. Oddly enough, F1236C enhanced stabilization of slow inactivation by both hastening entry into and delaying recovery from slow inactivation states. It is noteworthy that symmetric applications of QX-314 on both external and internal sides of F1236C mutant channels reduced recovery from use-dependent block, indicating an allosteric effect of external QX-314 binding on the recovery of availability of F1236C. These observations suggest that cysteine mutation in the SS1 region, particularly immediate adjacent to the DEKA ring, may lead to a structural rearrangement that alters binding of permanently charged QX-314 to its receptor. The results lend further support for a role for the selectivity filter region as a structural determinant for local anesthetic block.
Figures
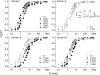
References
-
- Ahern CA, Eastwood AL, Dougherty DA, Horn R. (2008) Electrostatic contributions of aromatic residues in the local anesthetic receptor of voltage-gated sodium channels. Circ Res 102:86–94 - PubMed
-
- Alpert LA, Fozzard HA, Hanck DA, Makielski JC. (1989) Is there a second external lidocaine binding site on mammalian cardiac cells? Am J Physiol 257:H79–H84 - PubMed
-
- Baumgarten CM, Makielski JC, Fozzard HA. (1991) External site for local anesthetic block of cardiac Na+ channels. J Mol Cell Cardiol 23 (Suppl 1):85–93 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

