Cross talk between receptor guanylyl cyclase C and c-src tyrosine kinase regulates colon cancer cell cytostasis
- PMID: 19620276
- PMCID: PMC2747985
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00001-09
Cross talk between receptor guanylyl cyclase C and c-src tyrosine kinase regulates colon cancer cell cytostasis
Abstract
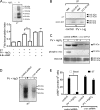
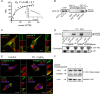
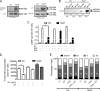
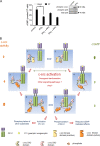
Increased activation of c-src seen in colorectal cancer is an indicator of a poor clinical prognosis, suggesting that identification of downstream effectors of c-src may lead to new avenues of therapy. Guanylyl cyclase C (GC-C) is a receptor for the gastrointestinal hormones guanylin and uroguanylin and the bacterial heat-stable enterotoxin. Though activation of GC-C by its ligands elevates intracellular cyclic GMP (cGMP) levels and inhibits cell proliferation, its persistent expression in colorectal carcinomas and occult metastases makes it a marker for malignancy. We show here that GC-C is a substrate for inhibitory phosphorylation by c-src, resulting in reduced ligand-mediated cGMP production. Consequently, active c-src in colonic cells can overcome GC-C-mediated control of the cell cycle. Furthermore, docking of the c-src SH2 domain to phosphorylated GC-C results in colocalization and further activation of c-src. We therefore propose a novel feed-forward mechanism of activation of c-src that is induced by cross talk between a receptor GC and a tyrosine kinase. Our findings have important implications in understanding the molecular mechanisms involved in the progression and treatment of colorectal cancer.
Figures


References
-
- Alessandro, R., A. M. Flugy, D. Russo, G. Stassi, A. De Leo, C. Corrado, G. Alaimo, and G. De Leo. 2005. Identification and phenotypic characterization of a subpopulation of T84 human colon cancer cells, after selection on activated endothelial cells. J. Cell Physiol. 203:261-272. - PubMed
-
- Anders, D. L., T. Blevins, G. Sutton, L. J. Chandler, and J. J. Woodward. 1999. Effects of c-Src tyrosine kinase on ethanol sensitivity of recombinant NMDA receptors expressed in HEK 293 cells. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 23:357-362. - PubMed
-
- Bakre, M. M., Y. Ghanekar, and S. S. Visweswariah. 2000. Homologous desensitization of the human guanylate cyclase C receptor. Cell-specific regulation of catalytic activity. Eur. J. Biochem. 267:179-187. - PubMed
-
- Bakre, M. M., and S. S. Visweswariah. 1997. Dual regulation of heat-stable enterotoxin-mediated cGMP accumulation in T84 cells by receptor desensitization and increased phosphodiesterase activity. FEBS Lett. 408:345-349. - PubMed
-
- Banker, N., B. M. Evers, M. R. Hellmich, and C. M. Townsend, Jr. 1996. The role of Src family kinases in the normal and neoplastic gastrointestinal tract. Surg. Oncol. 5:201-210. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
