Repression of ESR1 through actions of estrogen receptor alpha and Sin3A at the proximal promoter
- PMID: 19620290
- PMCID: PMC2738295
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00383-09
Repression of ESR1 through actions of estrogen receptor alpha and Sin3A at the proximal promoter
Abstract
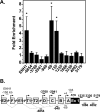
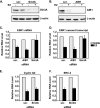
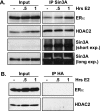
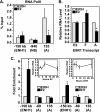
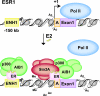
Gene expression results from the coordinated actions of transcription factor proteins and coregulators. Estrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that can both activate and repress the expression of genes. Activation of transcription by estrogen-bound ERalpha has been studied in detail, as has antagonist-induced repression, such as that which occurs by tamoxifen. How estrogen-bound ERalpha represses gene transcription remains unclear. In this report, we identify a new mechanism of estrogen-induced transcriptional repression by using the ERalpha gene, ESR1. Upon estrogen treatment, ERalpha is recruited to two sites on ESR1, one distal (ENH1) and the other at the proximal (A) promoter. Coactivator proteins, namely, p300 and AIB1, are found at both ERalpha-binding sites. However, recruitment of the Sin3A repressor, loss of RNA polymerase II, and changes in histone modifications occur only at the A promoter. Reduction of Sin3A expression by RNA interference specifically inhibits estrogen-induced repression of ESR1. Furthermore, an estrogen-responsive interaction between Sin3A and ERalpha is identified. These data support a model of repression wherein actions of ERalpha and Sin3A at the proximal promoter can overcome activating signals at distal or proximal sites and ultimately decrease gene expression.
Figures



References
-
- Alarid, E. T., N. Bakopoulos, and N. Solodin. 1999. Proteasome-mediated proteolysis of estrogen receptor: a novel component in autologous down-regulation. Mol. Endocrinol. 131522-1534. - PubMed
-
- An, J., R. C. Ribeiro, P. Webb, J. A. Gustafsson, P. J. Kushner, J. D. Baxter, and D. C. Leitman. 1999. Estradiol repression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha transcription requires estrogen receptor activation function-2 and is enhanced by coactivators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 9615161-15166. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayer, D. E., Q. A. Lawrence, and R. N. Eisenman. 1995. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell 80767-776. - PubMed
-
- Berger, S. L. 2007. The complex language of chromatin regulation during transcription. Nature 447407-412. - PubMed
-
- Berkenstam, A., H. Glaumann, M. Martin, J. A. Gustafsson, and G. Norstedt. 1989. Hormonal regulation of estrogen receptor messenger ribonucleic acid in T47D and MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 322-28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
