HIV-1 Nef promotes endocytosis of cell surface MHC class II molecules via a constitutive pathway
- PMID: 19620308
- PMCID: PMC7616452
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.0804014
HIV-1 Nef promotes endocytosis of cell surface MHC class II molecules via a constitutive pathway
Erratum in
- J Immunol. 2009 Dec 1;183(11):7611
Abstract
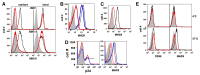
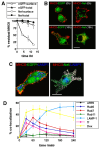
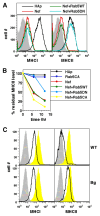
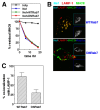
HIV-1 Nef has been reported to disrupt MHC class II (MHCII)-mediated Ag presentation by a dual strategy that comprises a reduction in cell surface levels of peptide-loaded mature MHCII molecules and a up-regulation of immature MHCII molecules. We show that Nef achieves relocation of MHCII away from the cell surface in monocytic cells by both delaying its transport to the cell surface and by accelerating endocytic removal of cell surface MHCII to a lysosomal compartment. Nef-induced MHCII endocytosis is cholesterol-sensitive but clathrin- and dynamin-independent. Internalized MHCII molecules traverse the early endosomal system and colocalize with pinocytic cargo before reaching lysosomes. Nef-triggered MHCII endocytosis requires Rab5 activity and lyst function, whereas lysosomal trafficking of internalized MHCII molecules requires Rab7 activity. We further show that a similar pathway can remove peptide-MHCII complexes from the surface of monocytic cells not expressing Nef. Our data suggest that Nef uses mechanisms involved in normal MHCII recycling and turnover to mediate the delivery of cell surface MHCII to a lysosomal destination. Thus, Nef-mediated endocytosis of MHCII provides a novel perspective on the regulation of normal MHCII trafficking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Kestler HW, III, Ringler DJ, Mori K, Panicali DL, Sehgal PK, Daniel MD, Desrosiers RC. Importance of the nef gene for maintenance of high virus loads and for development of AIDS. Cell. 1991;65:651–662. - PubMed
-
- Hanna Z, Kay DG, Rebai N, Guimond A, Jothy S, Jolicoeur P. Nef harbors a major determinant of pathogenicity for an AIDS-like disease induced by HIV-1 in transgenic mice. Cell. 1998;95:163–175. - PubMed
-
- Das SR, Jameel S. Biology of the HIV Nef protein. Indian J Med Res. 2005;121:315–332. - PubMed
-
- Arold ST, Baur AS. Dynamic Nef and Nef dynamics: how structure could explain the complex activities of this small HIV protein. Trends Biochem Sci. 2001;26:356–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

