Induction of periostin-like factor and periostin in forearm muscle, tendon, and nerve in an animal model of work-related musculoskeletal disorder
- PMID: 19620321
- PMCID: PMC2762884
- DOI: 10.1369/jhc.2009.954081
Induction of periostin-like factor and periostin in forearm muscle, tendon, and nerve in an animal model of work-related musculoskeletal disorder
Abstract
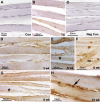
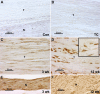
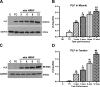
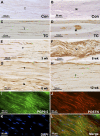
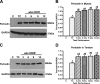
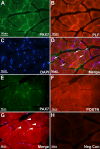
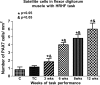
Work-related musculoskeletal disorders (WMSDs), also known as repetitive strain injuries of the upper extremity, frequently cause disability and impairment of the upper extremities. Histopathological changes including excess collagen deposition around myofibers, cell necrosis, inflammatory cell infiltration, and increased cytokine expression result from eccentric exercise, forced lengthening, exertion-induced injury, and repetitive strain-induced injury of muscles. Repetitive tasks have also been shown to result in tendon and neural injuries, with subsequent chronic inflammatory responses, followed by residual fibrosis. To identify mechanisms that regulate tissue repair in WMSDs, we investigated the induction of periostin-like factor (PLF) and periostin, proteins induced in other pathologies but not expressed in normal adult tissue. In this study, we examined the level of PLF and periostin in muscle, tendon, and nerve using immunohistochemistry and Western blot analysis. PLF increased with continued task performance, whereas periostin was constitutively expressed. PLF was located in satellite cells and/or myoblasts, which increased in number with continued task performance, supporting our hypothesis that PLF plays a role in muscle repair or regeneration. Periostin, on the other hand, was not present in satellite cells and/or myoblasts.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of TNF alpha and PLF in bone remodeling in a rat model of repetitive reaching and grasping.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Oct;225(1):152-67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22208. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20458732 Free PMC article.
-
Periostin-like-factor and Periostin in an animal model of work-related musculoskeletal disorder.Bone. 2009 Mar;44(3):502-12. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2008.11.012. Epub 2008 Nov 27. Bone. 2009. PMID: 19095091 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure-dependent increases in IL-1beta, substance P, CTGF, and tendinosis in flexor digitorum tendons with upper extremity repetitive strain injury.J Orthop Res. 2010 Mar;28(3):298-307. doi: 10.1002/jor.20984. J Orthop Res. 2010. PMID: 19743505 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological tissue changes associated with repetitive movement: a review of the evidence.Phys Ther. 2002 Feb;82(2):173-87. doi: 10.1093/ptj/82.2.173. Phys Ther. 2002. PMID: 11856068 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Prospects for the use of cells possessing myogenic potential in the treatment of skeletal muscle diseases: a review of research. Part 1 - satellite cells].Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 2015 Apr-Jun;59(2):88-98. Patol Fiziol Eksp Ter. 2015. PMID: 26571813 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Blocking CCN2 Reduces Progression of Sensorimotor Declines and Fibrosis in a Rat Model of Chronic Repetitive Overuse.J Orthop Res. 2019 Sep;37(9):2004-2018. doi: 10.1002/jor.24337. Epub 2019 Jun 20. J Orthop Res. 2019. PMID: 31041999 Free PMC article.
-
Blocking CCN2 Reduces Established Bone Loss Induced by Prolonged Intense Loading by Increasing Osteoblast Activity in Rats.JBMR Plus. 2023 Jun 16;7(9):e10783. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10783. eCollection 2023 Sep. JBMR Plus. 2023. PMID: 37701153 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TNF alpha and PLF in bone remodeling in a rat model of repetitive reaching and grasping.J Cell Physiol. 2010 Oct;225(1):152-67. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22208. J Cell Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20458732 Free PMC article.
-
Joint inflammation and early degeneration induced by high-force reaching are attenuated by ibuprofen in an animal model of work-related musculoskeletal disorder.J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:691412. doi: 10.1155/2011/691412. Epub 2011 Mar 3. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 21403884 Free PMC article.
-
Aging enhances serum cytokine response but not task-induced grip strength declines in a rat model of work-related musculoskeletal disorders.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011 Mar 29;12:63. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-12-63. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2011. PMID: 21447183 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allampallam K, Chakraborty J, Bose KK, Robinson J (1996) Explant culture, immunoflourescence and electron-microscopic study of flexor retinaculum in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Occup Environ Med 38:264–271 - PubMed
-
- Archambault JM, Hart DA, Herzog W (2001) Response of rabbit Achilles tendon to chronic repetitive loading. Connect Tissue Res 42:13–23 - PubMed
-
- Archambault JM, Jelinsky SA, Lake SP, Hill AA, Glaser DL, Soslowsky LJ (2007) Rat supraspinatus tendon expresses cartilage markers with overuse. J Orthop Res 25:617–624 - PubMed
-
- Bao S, Ouyang G, Bai X, Huang Z, Ma C, Liu M, Shao R, et al. (2004) Periostin potently promotes metastatic growth of colon cancer by augmenting cell survival via the Akt/PKB pathway. Cancer Cell 5:329–339 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

