In vivo MRI cell tracking: clinical studies
- PMID: 19620426
- PMCID: PMC2857985
- DOI: 10.2214/AJR.09.3107
In vivo MRI cell tracking: clinical studies
Abstract
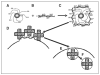
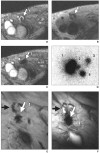
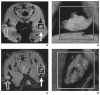
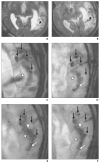
Objective: The purpose of this review is to describe the principles of MRI cell tracking with superparamagnetic iron oxides and the four clinical trials that have been performed.
Conclusion: Clinical MRI cell tracking is likely to become an important tool at the bedside once (stem) cell therapy becomes mainstream. The most prominent role of this technique probably will be verification of accurate cell delivery with MRI-guided injection, in which interventional radiologists will play a role in the near future. All clinical studies described as of this writing have been performed outside the United States.
Figures





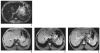

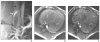
References
-
- Gilad AA, McMahon MT, Walczak P, et al. Artificial reporter gene providing MRI contrast based on proton exchange. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:217–219. - PubMed
-
- Cowper SE. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a review and exploration of the role of gadolinium. Adv Dermatol. 2007;23:131–154. - PubMed
-
- Morcos SK, Thomsen HS. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: more questions and some answers. Nephron Clin Pract. 2008;110:c24–c31. - PubMed
-
- Abraham JL, Thakral C. Tissue distribution and kinetics of gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur J Radiol. 2008;66:200–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

