Outcome of patients with early-stage breast cancer treated with doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy as a function of HER2 and TOP2A status
- PMID: 19620488
- PMCID: PMC2734394
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.20.1566
Outcome of patients with early-stage breast cancer treated with doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy as a function of HER2 and TOP2A status
Abstract
Purpose: Amplification and deletion of the TOP2A gene have been reported as positive predictive markers of response to anthracycline-based therapy. We determined the status of the HER2 and TOP2A genes in a large cohort of breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant doxorubicin (A) and cyclophosphamide (C).
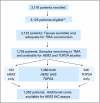
Patients and methods: TOP2A/CEP17 and HER2/CEP17 fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) were performed on tissue microarrays (TMAs) constructed from 2,123 of the 3,125 women with moderate-risk primary breast cancer who received equivalent doses of either concurrent adjuvant chemotherapy with A plus C (n = 1,592) or sequential A followed by C (n = 1,533).
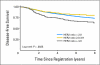
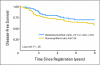
Results: An abnormal TOP2A genotype was identified for 153 (9.4%) of 1,626 patients (4.0% amplified; 5.4% deleted). An abnormal HER2 genotype was identified for 303 (20.4%) of 1,483 patients (18.8% amplified; 1.6% deleted). No significant differences in either overall survival (OS) or disease-free survival (DFS) were identified for TOP2A. In univariate analysis, OS and DFS rates were strongly and adversely associated only with higher levels of HER2 amplification (ratio > or = 4.0). Survival was not associated with low-level HER2 amplification (ratio > or = 2; OS hazard ratio [HR], 1.14; P = .39; DFS HR, 1.07; P = .62), but it was associated for a ratio > or = 4 (OS HR, 1.45; P = .03; DFS HR, 1.38; P = .033), in which analysis was adjusted for menopausal status, hormone receptor status, treatment, number of positive nodes, and tumor size.
Conclusion: In this population of patients with early-stage breast cancer who were treated with adjuvant AC chemotherapy, TOP2A abnormalities were not associated with outcome. HER2 high-level amplification was a prognostic marker in anthracycline-treated patients.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Comment in
-
Are HER2 and TOP2A useful as prognostic or predictive biomarkers for anthracycline-based adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer?J Clin Oncol. 2009 Aug 20;27(24):3875-6. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.8361. Epub 2009 Jul 20. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19620479 No abstract available.
References
-
- Levine MN, Pritchard KI, Bramwell VH, et al. Randomized trial comparing cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and fluorouracil with cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, and fluorouracil in premenopausal women with node-positive breast cancer: Update of National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Trial MA5. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5166–5170. - PubMed
-
- Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 2005;365:1687–1717. - PubMed
-
- Smith JA, Ngo H, Martin MC, et al. An evaluation of cytotoxicity of the taxane and platinum agents combination treatment in a panel of human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;98:141–145. - PubMed
-
- Henderson IC, Berry DA, Demetri GD, et al. Improved outcomes from adding sequential paclitaxel but not from escalating doxorubicin dose in an adjuvant chemotherapy regimen for patients with node-positive primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:976–983. - PubMed
-
- Pritchard KI, Messersmith H, Elavathil L, et al. HER-2 and topoisomerase II as predictors of response to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:736–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA22433/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58686/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58416/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21155/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76462/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA04920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA077658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA004919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA12644/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA20319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58415/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA32291/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA013612/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA031946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA049883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA63845/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA014028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA14028/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA074647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA58861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76132/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035261/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16385/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA032102/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046282/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45450/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46368/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA027057/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA046441/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA045377/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA35192/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA74647/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA020319/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA46113/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA038926/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA042777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA25224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77658/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA035119/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA42777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA52654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA067575/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA052654/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA025224/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA49883/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA76429/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA31946/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA063844/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA058861/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA37891/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 CA045560/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

