Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and epidermal growth factor receptor expression and benefit from lapatinib in a randomized trial of paclitaxel with lapatinib or placebo as first-line treatment in HER2-negative or unknown metastatic breast cancer
- PMID: 19620495
- PMCID: PMC2799151
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2008.18.1925
Estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2), and epidermal growth factor receptor expression and benefit from lapatinib in a randomized trial of paclitaxel with lapatinib or placebo as first-line treatment in HER2-negative or unknown metastatic breast cancer
Abstract
Purpose: Lapatinib is a dual inhibitor of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) with activity in HER2-amplified metastatic breast cancer (MBC). Its role in non-HER2-amplified MBC remains unclear. EGF30001, a phase III trial of lapatinib and paclitaxel versus paclitaxel and placebo, demonstrated lapatinib does not significantly benefit HER2-negative or HER2-unselected patients with MBC. Published data support interactions between steroid hormone and peptide growth factor signaling. We hypothesized that molecular subgroups may exist within EGF30001 that would benefit from lapatinib.
Methods: A blinded, retrospective biomarker evaluation was performed using immunohistochemistry to semiquantitate estrogen (ER), progesterone (PR), and EGFR expression. HER2 amplification was determined by fluorescent in situ hybridization. Effects of these biomarkers on event-free survival (EFS) were examined in patients with available tissue (n = 493).
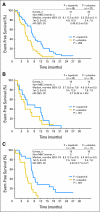
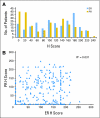
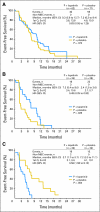
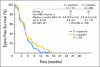
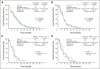
Results: Lapatinib improved median EFS in HER2-amplified, ER- or PR-positive MBC (n = 36; 5.7 v 4.5 months; P = .351); benefit was greater and statistically significant in HER2-amplified, ER-negative, PR-negative MBC (n = 42; 8.3 v 5.0 months; P = .007). In HER2-negative, ER-positive MBC, median EFS improvement varied by degree of PR expression (H-score): no benefit if PR-strong (n = 133; 9.3 v 7.3 months; P = .373), benefit if PR-weak (n = 50; 7.3 v 2.4 months; P = .026), and potential antagonism if PR-negative (n = 40; 3.7 v 7.2 months; P = .004). No benefit was seen in triple-negative MBC (n = 131; median EFS, 4.6 v 4.8 months; P = .255). EGFR expression was not correlated with benefit from lapatinib.
Conclusion: Although subgroups are small, these analyses support the hypothesis that semiquantitative determination of hormone receptor status may be a surrogate for EGFR and/or HER2 dependency.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest and author contributions are found at the end of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative ER and PgR assessment as predictors of benefit from lapatinib in postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 Feb 1;20(3):736-43. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1260. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24198242
-
Molecular Heterogeneity and Response to Neoadjuvant Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 Targeting in CALGB 40601, a Randomized Phase III Trial of Paclitaxel Plus Trastuzumab With or Without Lapatinib.J Clin Oncol. 2016 Feb 20;34(6):542-9. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.1268. Epub 2015 Nov 2. J Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26527775 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lapatinib combined with letrozole versus letrozole and placebo as first-line therapy for postmenopausal hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer.J Clin Oncol. 2009 Nov 20;27(33):5538-46. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.23.3734. Epub 2009 Sep 28. J Clin Oncol. 2009. PMID: 19786658 Clinical Trial.
-
Lapatinib: a dual inhibitor of human epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases.Clin Ther. 2008 Aug;30(8):1426-47. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.08.008. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18803986 Review.
-
A Roundtable Discussion of the Breast Cancer Therapy Expert Group (BCTEG): Clinical Developments and Practice Guidance on Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 (HER2)-positive Breast Cancer.Clin Breast Cancer. 2020 Jun;20(3):e251-e260. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2019.08.001. Epub 2019 Aug 21. Clin Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32139271 Review.
Cited by
-
RC48-ADC treatment for patients with HER2-expressing locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors: a real-world study.BMC Cancer. 2023 Nov 9;23(1):1083. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11593-9. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37946161 Free PMC article.
-
Positive expression of protein chromosome 9 open reading frame 86 (C9orf86) correlated with poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer patients.J Thorac Dis. 2016 Jul;8(7):1449-59. doi: 10.21037/jtd.2016.04.70. J Thorac Dis. 2016. PMID: 27499931 Free PMC article.
-
Application of a Biphasic Mathematical Model of Cancer Cell Drug Response for Formulating Potent and Synergistic Targeted Drug Combinations to Triple Negative Breast Cancer Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 27;12(5):1087. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051087. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32349331 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy, safety, pharmacokinetics and biomarker findings in patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer treated with lapatinib in combination with capecitabine: results from 51 Japanese patients treated in a clinical study.Breast Cancer. 2015 Mar;22(2):192-200. doi: 10.1007/s12282-013-0475-1. Epub 2013 May 21. Breast Cancer. 2015. PMID: 23689990 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Practical classification of triple-negative breast cancer: intratumoral heterogeneity, mechanisms of drug resistance, and novel therapies.NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020 Oct 16;6:54. doi: 10.1038/s41523-020-00197-2. eCollection 2020. NPJ Breast Cancer. 2020. PMID: 33088912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Johnston JB, Navaratnam S, Pitz MW, et al. Targeting the EGFR pathway for cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:3483–3492. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Clark GM, Wong SG, et al. Human breast cancer: Correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene. Science. 1987;235:177–182. - PubMed
-
- Slamon DJ, Godolphin W, Jones LA, et al. Studies of the HER-2/neu proto-oncogene in human breast and ovarian cancer. Science. 1989;244:707–712. - PubMed
-
- Salomon DS, Brandt R, Ciardiello F, et al. Epidermal growth factor-related peptides and their receptors in human malignancies. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1995;19:183–232. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Albanell J, Ruiz A, et al. Phase II and tumor pharmacodynamic study of gefitinib in patients with advanced breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5323–5333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

