A mediator of Rho-dependent invasion moonlights as a methionine salvage enzyme
- PMID: 19620624
- PMCID: PMC2758758
- DOI: 10.1074/mcp.M900178-MCP200
A mediator of Rho-dependent invasion moonlights as a methionine salvage enzyme
Abstract
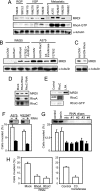
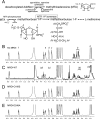
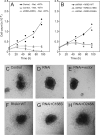
RhoA controls changes in cell morphology and invasion associated with cancer phenotypes. Cell lines derived from melanoma tumors at varying stages revealed that RhoA is selectively activated in cells of metastatic origin. We describe a functional proteomics strategy to identify proteins regulated by RhoA and report a previously uncharacterized human protein, named "mediator of RhoA-dependent invasion (MRDI)," that is induced in metastatic cells by constitutive RhoA activation and promotes cell invasion. In human melanomas, MRDI localization correlated with stage, showing nuclear localization in nevi and early stage tumors and cytoplasmic localization with plasma membrane accentuation in late stage tumors. Consistent with its role in promoting cell invasion, MRDI localized to cell protrusions and leading edge membranes in cultured cells and was required for cell motility, tyrosine phosphorylation of focal adhesion kinase, and modulation of actin stress fibers. Unexpectedly MRDI had enzymatic function as an isomerase that converts the S-adenosylmethionine catabolite 5-methylribose 1-phosphate into 5-methylribulose 1-phosphate. The enzymatic function of MRDI was required for methionine salvage from S-adenosylmethionine but distinct from its function in cell invasion. Thus, mechanisms used by signal transduction pathways to control cell movement have evolved from proteins with ancient function in amino acid metabolism.
Figures
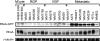



References
-
- Sauter E. R., Herlyn M. (1998) Molecular biology of human melanoma development and progression. Mol. Carcinog 23, 132–143 - PubMed
-
- Jaffe A. B., Hall A. (2005) Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 21, 247–269 - PubMed
-
- Clark E. A., Golub T. R., Lander E. S., Hynes R. O. (2000) Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC. Nature 406, 532–535 - PubMed
-
- Ikoma T., Takahashi T., Nagano S., Li Y. M., Ohno Y., Ando K., Fujiwara T., Fujiwara H., Kosai K. (2004) A definitive role of RhoC in metastasis of orthotopic lung cancer in mice. Clin. Cancer Res 10, 1192–1200 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA058187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA105796/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA118972/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32-GM008759/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F32-CA112847/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI060841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F32-CA105796/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM142607/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA126240/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI060841/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA126240/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008759/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA118972/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50-CA058187/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 CA112847/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

