Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis E virus-like particles based on the crystal structure
- PMID: 19620712
- PMCID: PMC2722322
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0903699106
Biological and immunological characteristics of hepatitis E virus-like particles based on the crystal structure
Abstract
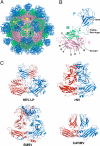
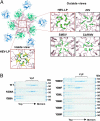
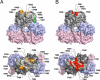
Hepatitis E virus (HEV) is a causative agent of acute hepatitis. The crystal structure of HEV-like particles (HEV-LP) consisting of capsid protein was determined at 3.5-A resolution. The capsid protein exhibited a quite different folding at the protruding and middle domains from the members of the families of Caliciviridae and Tombusviridae, while the shell domain shared the common folding. Tyr-288 at the 5-fold axis plays key roles in the assembly of HEV-LP, and aromatic amino acid residues are well conserved among the structurally related viruses. Mutational analyses indicated that the protruding domain is involved in the binding to the cells susceptive to HEV infection and has some neutralization epitopes. These structural and biological findings are important for understanding the molecular mechanisms of assembly and entry of HEV and also provide clues in the development of preventive and prophylactic measures for hepatitis E.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

